Page 695 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 695
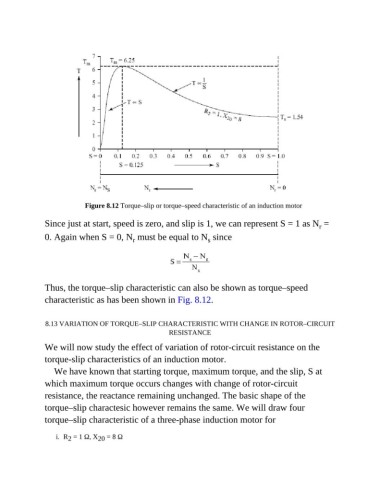
Figure 8.12 Torque–slip or torque–speed characteristic of an induction motor
Since just at start, speed is zero, and slip is 1, we can represent S = 1 as N =
r
0. Again when S = 0, N must be equal to N since
r
s
Thus, the torque–slip characteristic can also be shown as torque–speed
characteristic as has been shown in Fig. 8.12.
8.13 VARIATION OF TORQUE–SLIP CHARACTERISTIC WITH CHANGE IN ROTOR–CIRCUIT
RESISTANCE
We will now study the effect of variation of rotor-circuit resistance on the
torque-slip characteristics of an induction motor.
We have known that starting torque, maximum torque, and the slip, S at
which maximum torque occurs changes with change of rotor-circuit
resistance, the reactance remaining unchanged. The basic shape of the
torque–slip charactesic however remains the same. We will draw four
torque–slip characteristic of a three-phase induction motor for
i. R = 1 Ω, X = 8 Ω
20
2