Page 214 - Fiber Optic Communications Fund
P. 214
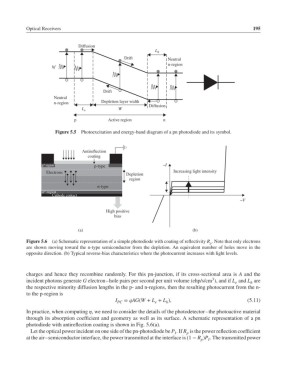
Optical Receivers 195
Diffusion
L h
Drift Neutral
n-region
hf
Drift
Neutral
n-region Depletion layer width
Diffusion
L e W
p Active region n
Figure 5.5 Photoexcitation and energy-band diagram of a pn photodiode and its symbol.
Antireflection
coating
p + region p-type ‒I
Electrons Depletion Increasing light intensity
region
n-type
n + region
Cathode contact
‒V
High positive
bias
(a) (b)
Figure 5.6 (a) Schematic representation of a simple photodiode with coating of reflectivity R . Note that only electrons
p
are shown moving toward the n-type semiconductor from the depletion. An equivalent number of holes move in the
opposite direction. (b) Typical reverse-bias characteristics where the photocurrent increases with light levels.
charges and hence they recombine randomly. For this pn-junction, if its cross-sectional area is A and the
3
incident photons generate G electron–hole pairs per second per unit volume (ehp/s/cm ), and if L and L are
e
h
the respective minority diffusion lengths in the p- and n-regions, then the resulting photocurrent from the n-
to the p-region is
I PC = qAG(W + L + L ), (5.11)
h
e
In practice, when computing , we need to consider the details of the photodetector–the photoactive material
through its absorption coefficient and geometry as well as its surface. A schematic representation of a pn
photodiode with antireflection coating is shown in Fig. 5.6(a).
Let the optical power incident on one side of the pn-photodiode be P .If R is the power reflection coefficient
I
p
at the air–semiconductor interface, the power transmitted at the interface is (1 − R )P . The transmitted power
p
I