Page 352 - Fiber Optic Communications Fund
P. 352
Transmission System Design 333
Using Eq. (7.135), we find
√
P in
Q =
f
4 ASE,eq e
√
1.26 × 10 −3
=
4 × 1.17 × 10 −15 × 7 × 10 9
= 6.2
Exercises
7.1 In a fiber-optic system based on OOK as shown in Fig. 7.1, fiber loss = 0.21 dB/km, length
∘
L = 120 km, peak power at the transmitter = 2dBm, T = 23 C, R = 100 Ω, B = 7 GHz, and
L
e
R = 1.1 A/W. Find (a) the peak power at the receiver, (b) the Q-factor, and (c) the BER.
−7
(Ans: (a) −23.3 dBm, (b) 4.89, (c) 4.84 × 10 .)
7.2 In a 1.55-μm fiber-optic system based on OOK as shown in Fig. 7.5, the peak transmitter power P =
in
2 dBm, fiber loss coefficient = 0.2dB/km, T = 290 K, R = 1000 Ω, R = 1A/W, B = 20 GHz, B =
L o e
7.5 GHz, gain and n of the preamplifier are 25 dB and 1.5, respectively. Find the maximum achievable
sp
−9
transmission distance to have a BER of 10 .
(Ans: 190.5 km.)
7.3 Ina1.55-μm coherent fiber-optic system based on PSK, as shown in Fig. 7.7, find the lower limit on
the LO power such that the shot noise dominates the thermal noise and the difference between the
Q-factor given by Eq. (7.62) and the exact Q-factor is ≤ 2.5%. The mean received power =−45 dBm,
T = 293 K, = 0.8, R = 200 Ω, and B = 7 GHz.
L e
(Ans: 5 mW.)
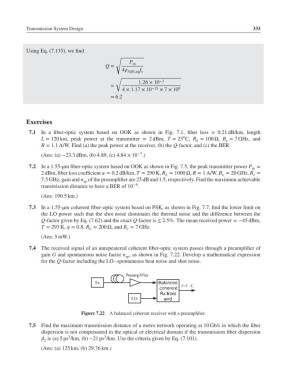
7.4 The received signal of an unrepeatered coherent fiber-optic system passes through a preamplifier of
gain G and spontaneous noise factor n , as shown in Fig. 7.22. Develop a mathematical expression
sp
for the Q-factor including the LO–spontaneous beat noise and shot noise.
Figure 7.22 A balanced coherent receiver with a preamplifier.
7.5 Find the maximum transmission distance of a metro network operating at 10 Gb/s in which the fiber
dispersion is not compensated in the optical or electrical domain if the transmission fiber dispersion
2
2
is (a) 5 ps /km, (b) −21 ps /km. Use the criteria given by Eq. (7.101).
2
(Ans: (a) 125 km, (b) 29.76 km.)