Page 368 - Fiber Optic Communications Fund
P. 368
Performance Analysis 349
8.3.2 On–Off Keying
In this case, the optical field envelope may be written as
s(t)= s (t) for bit ‘1’ (8.108)
1
= 0 for bit ‘0’ (8.109)
Therefore,
E = 0 and E 10 = 0. (8.110)
0
The average energy is
E = E ∕2. (8.111)
1
av
Using Eqs. (8.111) and (8.110), Eqs. (8.38) and (8.39) can be written as
homo homo
= 4E ∕N = 4 (8.112)
max av 0
and
(√ )
1 homo
P = erfc (8.113)
b
2 2
exp (− homo ∕2) homo
≅ when ≫ 1. (8.114)
√
2 homo
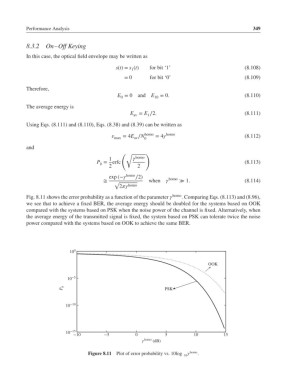
Fig. 8.11 shows the error probability as a function of the parameter homo . Comparing Eqs. (8.113) and (8.96),
we see that to achieve a fixed BER, the average energy should be doubled for the systems based on OOK
compared with the systems based on PSK when the noise power of the channel is fixed. Alternatively, when
the average energy of the transmitted signal is fixed, the system based on PSK can tolerate twice the noise
power compared with the systems based on OOK to achieve the same BER.
10 0
OOK
10 *5
P b PSK
10 *10
10 *15
*10 *5 0 5 10 15
γ homo (dB)
Figure 8.11 Plot of error probability vs. 10log homo .
10