Page 510 - Fiber Optic Communications Fund
P. 510
Nonlinear Effects in Fibers 491
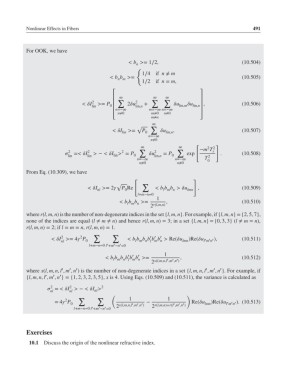
For OOK, we have
< b >= 1∕2, (10.504)
n
{
1∕4 if n ≠ m
< b b >= (10.505)
n m
1∕2 if n = m,
⎡ ⎤
⎢ ∞ ∑ ∑ ⎥
∞
∞
∑
<I 2 >= P ⎢ 2u 2 + u u ⎥ , (10.506)
lin 0 lin,n lin,m lin,n
⎢ ⎥
n=−∞ m=−∞ n=−∞
⎢ n≠0 m≠0 n≠0 ⎥
⎣ m≠n ⎦
∞
√ ∑
<I >= P u , (10.507)
lin 0 lin,n
n=−∞
n≠0
[ ]
∞ ∞ 2 2
∑ ∑ −m T
2 2 2 2 s
=<I > − <I > = P u = P exp . (10.508)
lin lin lin 0 lin,n 0 2
n=−∞ n=−∞ T 0
n≠0 n≠0
From Eq. (10.309), we have
[ ]
√ ∑
<I >= 2 P Re < b b b >u lmn , (10.509)
l m n
nl
0
l+m−n=0
1
< b b b >= , (10.510)
l m n
2 r(l,m,n)
where r(l, m, n) is the number of non-degenerate indices in the set {l, m, n}. For example, if {l, m, n}={2, 5, 7},
none of the indices are equal (l ≠ m ≠ n) and hence r(l, m, n)= 3; in a set {l, m, n}={0, 3, 3} (l ≠ m = n),
r(l, m, n)= 2; if l = m = n, r(l, m, n)= 1.
∑ ∑ ′ ′ ′
2
2
<I >= 4 P < b b b b b b > Re(u )Re(u ′ m ′ n ′), (10.511)
nl 0 l m n l m n lmn l
l+m−n=0 l ′ +m ′ −n ′ =0
′ ′ ′ 1
< b b b b b b >= , (10.512)
l m n l m n
2 x(l,m,n,l ′ ,m ′ ,n ′ )
′
′
′
′
′
′
where x(l, m, n, l , m , n ) is the number of non-degenerate indices in a set {l, m, n, l , m , n }. For example, if
′
′
′
{l, m, n, l , m , n }={1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 5}, x is 4. Using Eqs. (10.509) and (10.511), the variance is calculated as
2
2
= <I > − <I > 2
nl nl nl
( )
∑ ∑ 1 1
2
= 4 P 0 x(l,m,n,l ′ ,m ′ ,n ′ ) − r(l,m,n)+r(l ′ ,m ′ ,n ′ ) Re(u lmn )Re(u ′ m ′ n ′). (10.513)
l
l+m−n=0 l ′ +m ′ −n ′ =0 2 2
Exercises
10.1 Discuss the origin of the nonlinear refractive index.