Page 260 - Introduction to Business
P. 260
234 PART 2 Managing Business Behavior
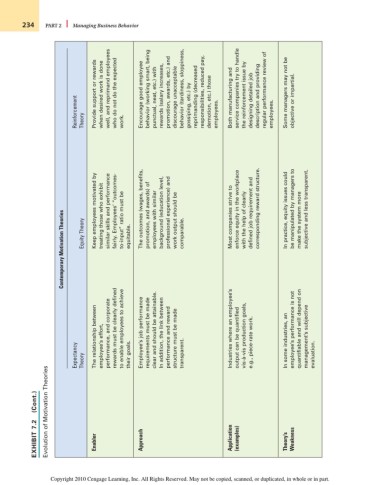
Provide support or rewards when desired work is done well, and reprimand employees who do not do the expected Encourage good employee behavior (working smart, being punctual, neat, etc.) with rewards (salary increases, promotion, awards, etc.) and discourage unacceptable behavior (tardiness, sloppiness, reprimanding (decreased responsibilities, reduced pay, demotion, etc.) those Both manufacturing and service companies try to handle the reinforcemen
Reinforcement Theory work. gossiping, etc.) by employees. employees.
Contemporary Motivation Theories Equity Theory Keep employees motivated by treating those who exhibit similar skills and performance fairly. Employees’ “outcomes- to-input” ratio must be equitable. The outcomes (wages, benefits, promotion, and awards) of employees with similar background (education level, professional experience) and work output should be comparable. Most companies strive to equity in the workplace enforce with the help of clearly defined j
The relationship between employee’s effort, performance, and corporate rewards must be clearly defined to enable employees to achieve Employee’s job performance requirements must be made clear and should be attainable. In addition, the link between performance and reward structure must be made Industries where an employee’s output can be quantified vis-à-vis production goals, e.g., piece-rate work. In some industries, an employee’s performance is
Expectancy Theory their goals. transparent. evaluation.
(Cont.) Evolution of Motivation Theories
EXHIBIT 7.2 Enabler Approach Application (examples) Theory’s Weakness
Copyright 2010 Cengage Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.