Page 491 - Introduction to Business
P. 491
CHAPTER 13 Financial Management of the Firm and Investment Management 465
Investors use the levels of interest rates on government bonds, known as Treasury
securities in the United States, to monitor interest rate risk. As movements in inter-
est rate levels become more volatile, bond prices increasingly fluctuate. In general,
when interest rates go up, bond prices go down, and vice versa.
Liquidity risk concerns the problem of selling a security quickly for a fair mar- liquidity risk The risk that a security
ket price. Some bonds and stocks are illiquid in the sense that an investor must sub- cannot be sold quickly for a fair market
price
stantially lower the sales price to attract a buyer. Bonds and stocks issued by large
firms tend to be more liquid than those issued by smaller firms.
Tax risk is the exposure of earnings from an investment to government taxation. tax risk The exposure of earnings from
Dividend and coupon payments are subject to income taxes, which are typically an investment to government taxation,
including income and capital gains taxes
higher than capital gains taxes. Investors in high tax brackets may well be expected
to seek investments with lower dividend and coupon payments and higher capital
gains. Bonds issued by state and local governments, known as municipal securities, municipal securities Debt securities
pay coupon interest payments that are exempt from income taxes. Again, investors issued by state and local governments
to raise funds, with coupon payments
in high tax brackets can be expected to purchase these securities.
that are exempt from federal income
Firm-specific risk encompasses any risk that faces the individual firm that is taxes
not related to market, liquidity, and tax risks. Examples are default risk, competition firm-specific risk Any risk that is
from other firms in the industry, legal actions against the firm, agency problems particular to an individual firm and not
related to market, liquidity, and tax risks
between managers and shareholders, scandals that damage the firm’s reputation,
that affect all firms
technological adaptability of the firm, management competence, and marketing
effectiveness. These are firm-specific risks that pertain to how the firm manages its
business activities.
Reinvestment risk arises when an investor receives a payment on a security and reinvestment risk The risk an investor
decides to buy other securities with the proceeds. The problem is that the new faces when payments on high-earning
securities are received and are
securities may have lower earning power than the old securities. Dividend and
subsequently used to buy other
coupon payments can be difficult to always reinvest at good rates of return. When securities that have lower earnings
interest rates are rising, coupons can be reinvested at higher interest rates than pre-
viously. Alternatively, in recent years interest rates have fallen to historically low lev-
els, which means that coupons are reinvested in low-earning bonds. Also, dividends
can be reinvested in stocks when the S&P 500 index is rising. However, if the stock
market as a whole is experiencing falling prices, reinvesting dividends in stocks
would result in capital losses. These same concepts apply to payments of bond
principal or sales of stocks and bonds. Reinvestment risk can work for or against an total risk The sum of all risks associated
with a security, which can be measured
investor. as the volatility of the security’s price
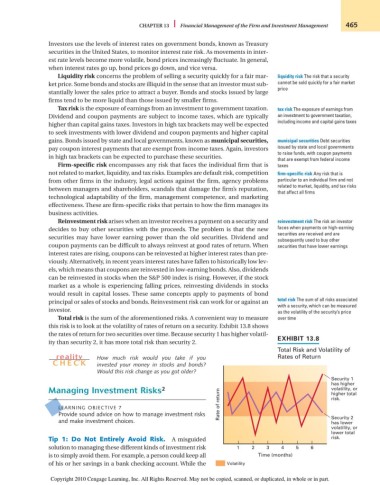
Total risk is the sum of the aforementioned risks. A convenient way to measure over time
this risk is to look at the volatility of rates of return on a security. Exhibit 13.8 shows
the rates of return for two securities over time. Because security 1 has higher volatil-
EXHIBIT 13.8
ity than security 2, it has more total risk than security 2.
Total Risk and Volatility of
reality How much risk would you take if you Rates of Return
CH ECK invested your money in stocks and bonds?
Would this risk change as you got older?
Security 1
has higher
Managing Investment Risks 2 volatility, or
higher total
risk.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE 7 Rate of return
Provide sound advice on how to manage investment risks
and make investment choices. Security 2
has lower
volatility, or
lower total
Tip 1: Do Not Entirely Avoid Risk. A misguided risk.
solution to managing these different kinds of investment risk 1 2 3 4 5 6
is to simply avoid them. For example, a person could keep all Time (months)
of his or her savings in a bank checking account. While the Volatility
Copyright 2010 Cengage Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.