Page 493 - Introduction to Business
P. 493
CHAPTER 13 Financial Management of the Firm and Investment Management 467
earnings from investments in securities would likely lead to financial security after
about 20 to 30 years. What if their disposable income were $40,000? A 10 percent
savings rate per year would mean that they would save and invest $4000 each year.
Over 20 years, by investing these savings regularly over time as recommended in
Tip 3, this level of investment would yield $229,100. Assuming that the savers paid total net worth The sum of the market
off a home valued at $100,000 over this 20 years and accumulated $20,000 in other values of all financial and real assets
owned, including cash, bonds, stocks,
savings, their total net worth would be around $350,000. If they saved for 40 years land, buildings, and other property
instead of 20 years, their total net worth would rise to $1,770,370 $100,000 diversification Buying different
$20,000 $1,890,370. These rough figures reveal that a sure way to earn more is financial and real assets whose prices
simply to save and invest more. or values have different patterns of
movement up and down over time, such
that the total risk or volatility is reduced
Tip 5: Diversify Securities. Diversification is a powerful tool used to for the entire portfolio of assets
3
decrease investment risk. It is important to recognize that diversification cannot
increase investment returns, only decrease risk per unit
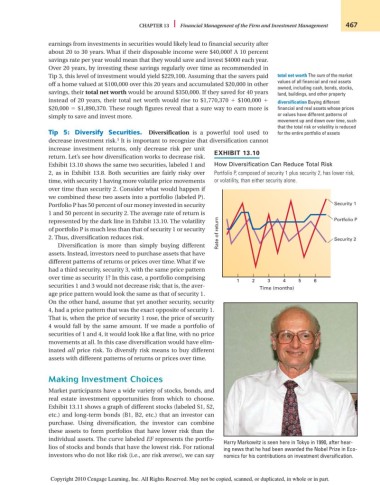
return. Let’s see how diversification works to decrease risk. EXHIBIT 13.10
Exhibit 13.10 shows the same two securities, labeled 1 and How Diversification Can Reduce Total Risk
2, as in Exhibit 13.8. Both securities are fairly risky over Portfolio P, composed of security 1 plus security 2, has lower risk,
time, with security 1 having more volatile price movements or volatility, than either security alone.
over time than security 2. Consider what would happen if
we combined these two assets into a portfolio (labeled P).
Portfolio P has 50 percent of our money invested in security Security 1
1 and 50 percent in security 2. The average rate of return is
represented by the dark line in Exhibit 13.10. The volatility Portfolio P
of portfolio P is much less than that of security 1 or security
2. Thus, diversification reduces risk. Rate of return Security 2
Diversification is more than simply buying different
assets. Instead, investors need to purchase assets that have
different patterns of returns or prices over time. What if we
had a third security, security 3, with the same price pattern
over time as security 1? In this case, a portfolio comprising
1 2 3 4 5 6
securities 1 and 3 would not decrease risk; that is, the aver-
Time (months)
age price pattern would look the same as that of security 1.
On the other hand, assume that yet another security, security
4, had a price pattern that was the exact opposite of security 1.
That is, when the price of security 1 rose, the price of security
4 would fall by the same amount. If we made a portfolio of
securities of 1 and 4, it would look like a flat line, with no price
movements at all. In this case diversification would have elim-
inated all price risk. To diversify risk means to buy different
assets with different patterns of returns or prices over time.
Making Investment Choices
Market participants have a wide variety of stocks, bonds, and
real estate investment opportunities from which to choose.
Exhibit 13.11 shows a graph of different stocks (labeled S1, S2,
etc.) and long-term bonds (B1, B2, etc.) that an investor can
purchase. Using diversification, the investor can combine
these assets to form portfolios that have lower risk than the
individual assets. The curve labeled EF represents the portfo-
Harry Markowitz is seen here in Tokyo in 1990, after hear-
lios of stocks and bonds that have the lowest risk. For rational ing news that he had been awarded the Nobel Prize in Eco-
investors who do not like risk (i.e., are risk averse), we can say nomics for his contributions on investment diversification.
Copyright 2010 Cengage Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part.