Page 18 - tmp_Neat
P. 18
severity injury or non-injury to fatal injury. On the other hand, the unordered multinomial
discrete outcome does not consider ordinal severity injury datasets.
Generally, the injury severity of crashes is categorised as fatal, incapacitating injury, non-
incapacitating injury, possible injury, and property damage only. In general, a sample size
smaller than 1000 should not be used for crash severity model development, and sample sizes
should be larger than 1000 for the ordered logit model and 2000 for the multinomial logit
model (Ye & Lord 2014).
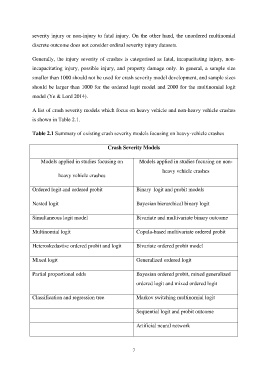
A list of crash severity models which focus on heavy vehicle and non-heavy vehicle crashes
is shown in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1 Summary of existing crash severity models focusing on heavy-vehicle crashes
Crash Severity Models
Models applied in studies focusing on Models applied in studies focusing on non-
heavy vehicle crashes
heavy vehicle crashes
Ordered logit and ordered probit Binary logit and probit models
Nested logit Bayesian hierarchical binary logit
Simultaneous logit model Bivariate and multivariate binary outcome
Multinomial logit Copula-based multivariate ordered probit
Heteroskedastisc ordered probit and logit Bivariate ordered probit model
Mixed logit Generalized ordered logit
Partial proportional odds Bayesian ordered probit, mixed generalized
ordered logit and mixed ordered logit
Classification and regression tree Markov switching multinomial logit
Sequential logit and probit outcome
Artificial neural network
7