Page 196 - Microsoft Word - 00 P1 IW Prelims.docx
P. 196
Chapter 12
Synergy
2.1 Definition of synergy
Synergy may be defined as two or more entities coming together to
produce a result not independently obtainable.
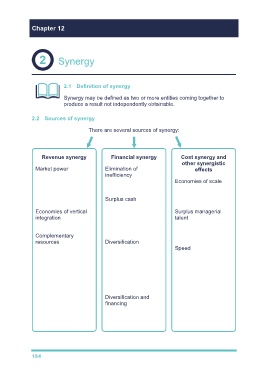
2.2 Sources of synergy
There are several sources of synergy:
Revenue synergy Financial synergy Cost synergy and
other synergistic
Market power – Elimination of effects
horizontal combinations inefficiency – If the
may give monopoly victim company is badly Economies of scale –
power that can increase managed. can occur in the
profitability (but beware production, marketing
competition authorities). Surplus cash – or finance areas.
acquisition uses surplus
Economies of vertical cash if increased Surplus managerial
integration – 'cutting out dividends are not talent – the acquisition
the middle man'. considered to be of inefficient companies
appropriate. is a good way to utilise
Complementary skilled managers.
resources – e.g. Diversification –
combining an R&D reduces risk, so even if Speed – acquisition is
company with a the earnings stay the usually much faster
company strong in same (i.e. no operating than organic growth.
marketing could lead to economies), there
gains. could still be an
increase in value of the
company.
Diversification and
financing – variability of
operating cash flows
may be reduced - more
attractive to lenders.
184