Page 47 - FINAL CFA II SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 9
P. 47
LOS 36.h: Explain how interest rate volatility
affects option-adjusted spreads. READING 36: VALUATION AND ANALYSIS: BONDS WITH EMBEDDED OPTIONS
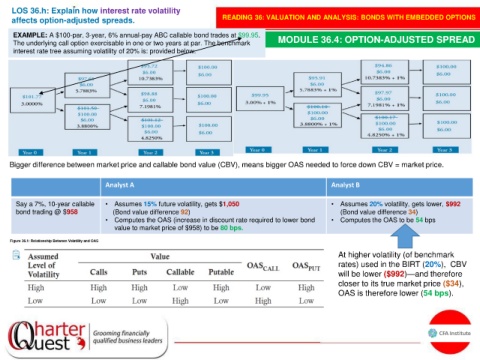
EXAMPLE: A $100-par, 3-year, 6% annual-pay ABC callable bond trades at $99.95. MODULE 36.4: OPTION-ADJUSTED SPREAD
The underlying call option exercisable in one or two years at par. The benchmark
interest rate tree assuming volatility of 20% is: provided below.
Bigger difference between market price and callable bond value (CBV), means bigger OAS needed to force down CBV = market price.
Analyst A Analyst B
Say a 7%, 10-year callable • Assumes 15% future volatility, gets $1,050 • Assumes 20% volatility, gets lower, $992
bond trading @ $958 (Bond value difference 92) (Bond value difference 34)
• Computes the OAS (increase in discount rate required to lower bond • Computes the OAS to be 54 bps
value to market price of $958) to be 80 bps.
At higher volatility (of benchmark
rates) used in the BIRT (20%), CBV
will be lower ($992)—and therefore
closer to its true market price ($34),
OAS is therefore lower (54 bps).