Page 3 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 3
LOS 34.a: Describe relationships among spot rates, READING 34: THE TERM STRUCTURE AND
forward rates, yield to maturity, expected and realized INTEREST RATE DYNAMICS
returns on bonds, and the shape of the yield curve.
MODULE 34.1: SPOT AND FORWARD RATES, PART 1
SPOT RATES
If a zero-coupon bond pays no coupon, then it must promise a single sum
(FV) that is higher than par (PV) to attract investment: the implied rate
separating PV and FV is ‘interest / YTM’ (called spot rate, S in this case).
T
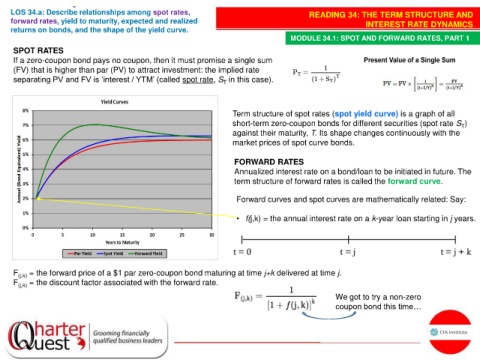
Term structure of spot rates (spot yield curve) is a graph of all
short-term zero-coupon bonds for different securities (spot rate S )
T
against their maturity, T. Its shape changes continuously with the
market prices of spot curve bonds.
FORWARD RATES
Annualized interest rate on a bond/loan to be initiated in future. The
term structure of forward rates is called the forward curve.
Forward curves and spot curves are mathematically related: Say:
• f(j,k) = the annual interest rate on a k-year loan starting in j years.
F (j,k) = the forward price of a $1 par zero-coupon bond maturing at time j+k delivered at time j.
F (j,k) = the discount factor associated with the forward rate.
We got to try a non-zero
coupon bond this time…