Page 7 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 7
LOS 34.b: Describe the forward pricing and forward
rate models and calculate forward and spot prices READING 34: THE TERM STRUCTURE AND
and rates using those models. INTEREST RATE DYNAMICS
MODULE 34.1: SPOT AND FORWARD RATES, PART 1
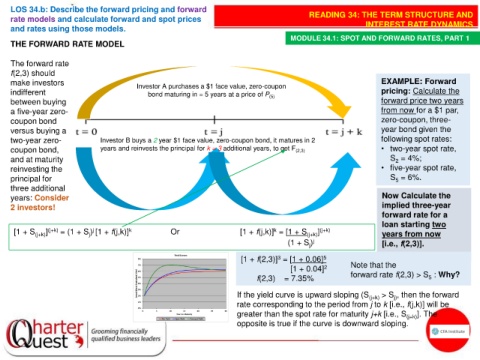
THE FORWARD RATE MODEL
The forward rate
f(2,3) should
make investors Investor A purchases a $1 face value, zero-coupon EXAMPLE: Forward
indifferent bond maturing in = 5 years at a price of P (5) pricing: Calculate the
between buying forward price two years
a five-year zero- from now for a $1 par,
coupon bond zero-coupon, three-
versus buying a year bond given the
two-year zero- Investor B buys a 2 year $1 face value, zero-coupon bond, it matures in 2 following spot rates:
coupon bond, years and reinvests the principal for k = 3 additional years, to get F (2,3) • two-year spot rate,
and at maturity S = 4%;
2
reinvesting the • five-year spot rate,
principal for S = 6%.
5
three additional
years: Consider Now Calculate the
2 investors! implied three-year
forward rate for a
loan starting two
k
j
[1 + S (j+k) ] (j+k) = (1 + S ) [1 + f(j,k)] k Or [1 + f(j,k)] = [1 + S (j+k) ] (j+k) years from now
j
(1 + S ) j [i.e., f(2,3)].
j
[1 + f(2,3)] = [1 + 0.06] 5
3
[1 + 0.04] 2 Note that the
f(2,3) = 7.35% forward rate f(2,3) > S : Why?
5
If the yield curve is upward sloping (S (j+k) > S , then the forward
j)
rate corresponding to the period from j to k [i.e., f(j,k)] will be
greater than the spot rate for maturity j+k [i.e., S (j+k) ]. The
opposite is true if the curve is downward sloping.