Page 6 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 6
LOS 34.b: Describe the forward pricing and forward
rate models and calculate forward and spot prices READING 34: THE TERM STRUCTURE AND
and rates using those models. INTEREST RATE DYNAMICS
MODULE 34.1: SPOT AND FORWARD RATES, PART 1
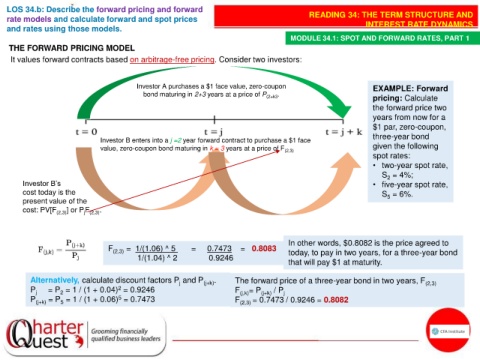
THE FORWARD PRICING MODEL
It values forward contracts based on arbitrage-free pricing. Consider two investors:
Investor A purchases a $1 face value, zero-coupon EXAMPLE: Forward
bond maturing in 2+3 years at a price of P (2+k3 . pricing: Calculate
the forward price two
years from now for a
$1 par, zero-coupon,
three-year bond
Investor B enters into a j =2 year forward contract to purchase a $1 face
value, zero-coupon bond maturing in k = 3 years at a price of F (2,3) given the following
spot rates:
• two-year spot rate,
S = 4%;
2
Investor B’s • five-year spot rate,
cost today is the S = 6%.
present value of the 5
cost: PV[F (2,3) ] or PF .
j (2,3)
In other words, $0.8082 is the price agreed to
F (2,3) = 1/(1.06) ^ 5 = 0.7473 = 0.8083 today, to pay in two years, for a three-year bond
1/(1.04) ^ 2 0.9246
that will pay $1 at maturity.
Alternatively, calculate discount factors P and P (j+k) . The forward price of a three-year bond in two years, F (2,3)
j
P j = P = 1 / (1 + 0.04) = 0.9246 F (j,k) = P (j+k) / P j
2
2
5
P (j+k) = P = 1 / (1 + 0.06) = 0.7473 F (2,3) = 0.7473 / 0.9246 = 0.8082
5