Page 7 - FINAL CFA SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 2
P. 7
LOS 6.e: Calculate and interpret the FV & PV of a Session Unit 2: The Time Value of Money
single sum of money, an ordinary annuity, an
annuity due, a perpetuity (PV only), and a series
of unequal cash flows.
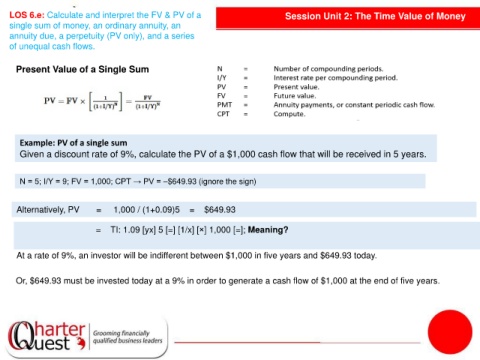
Present Value of a Single Sum
Example: PV of a single sum
Given a discount rate of 9%, calculate the PV of a $1,000 cash flow that will be received in 5 years.
N = 5; I/Y = 9; FV = 1,000; CPT → PV = –$649.93 (ignore the sign)
Alternatively, PV = 1,000 / (1+0.09)5 = $649.93
= TI: 1.09 [yx] 5 [=] [1/x] [×] 1,000 [=]; Meaning?
At a rate of 9%, an investor will be indifferent between $1,000 in five years and $649.93 today.
Or, $649.93 must be invested today at a 9% in order to generate a cash flow of $1,000 at the end of five years.