Page 8 - FINAL CFA SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 2
P. 8
LOS 6.e: Calculate and interpret the FV & PV a Session Unit 2: The Time Value of Money
single sum of money, an ordinary annuity, an
annuity due, a perpetuity (PV only), and a
series of unequal cash flows.
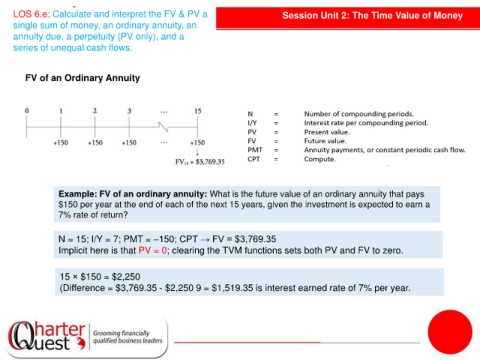
FV of an Ordinary Annuity
Example: FV of an ordinary annuity: What is the future value of an ordinary annuity that pays
$150 per year at the end of each of the next 15 years, given the investment is expected to earn a
7% rate of return?
N = 15; I/Y = 7; PMT = –150; CPT → FV = $3,769.35
Implicit here is that PV = 0; clearing the TVM functions sets both PV and FV to zero.
15 × $150 = $2,250
(Difference = $3,769.35 - $2,250 9 = $1,519.35 is interest earned rate of 7% per year.