Page 109 - Microsoft Word - 00 P1 IW Prelims.docx
P. 109
Financial performance measures in the private sector
2.2 Measuring profitability
The primary objective of a profit seeking company is to maximise
profitability. A business needs to make a profit to be able to provide a
return to any investors and to be able to grow the business by
reinvestment.
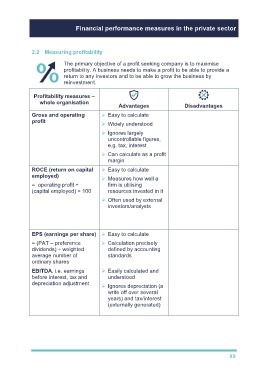
Profitability measures –
whole organisation
Advantages Disadvantages
Gross and operating Easy to calculate Poor correlation to
profit shareholder wealth
Widely understood
Can be distorted by
Ignores largely
uncontrollable figures, accounting policies
e.g. tax, interest
Can calculate as a profit
margin
ROCE (return on capital Easy to calculate Poor correlation to
employed) shareholder wealth
Measures how well a
= operating profit ÷ firm is utilising Can be distorted by
(capital employed) × 100 resources invested in it accounting policies
Often used by external Possible dysfunctional
investors/analysts behaviour and/or a
cutting back in
investment if used as a
performance target
EPS (earnings per share) Easy to calculate Poor correlation to
shareholder wealth
= (PAT – preference Calculation precisely
dividends) ÷ weighted defined by accounting Accounting treatment
average number of standards may distort measure
ordinary shares
EBITDA, i.e. earnings Easily calculated and Poor correlation to
before interest, tax and understood shareholder wealth
depreciation adjustment
Ignores depreciation (a Ignores changes to
write off over several working capital or
years) and tax/interest amount of non-current
(externally generated) asset replacement
needed
99