Page 86 - Microsoft Word - 00 CIMA F1 Prelims STUDENT 2018.docx
P. 86
Chapter 8
Procedure for establishing the maximum price of a product
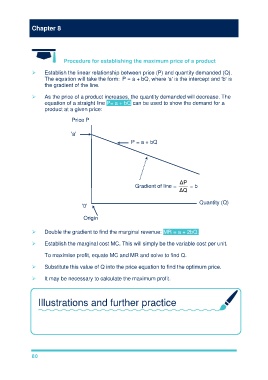
Establish the linear relationship between price (P) and quantity demanded (Q).
The equation will take the form: P = a + bQ, where 'a' is the intercept and 'b' is
the gradient of the line.
As the price of a product increases, the quantity demanded will decrease. The
equation of a straight line P= a + bQ can be used to show the demand for a
product at a given price:
Price P
'a'
P = a + bQ
Gradient of line = = b
Quantity (Q)
'0'
Origin
Double the gradient to find the marginal revenue: MR = a + 2bQ.
Establish the marginal cost MC. This will simply be the variable cost per unit.
To maximise profit, equate MC and MR and solve to find Q.
Substitute this value of Q into the price equation to find the optimum price.
It may be necessary to calculate the maximum profit.
Illustrations and further practice
Now read the illustration ‘The MR = MC diagram’ from Chapter 8 and attempt
examples 1 to 4.
80