Page 218 - ACCESS BANK ANNUAL REPORTS_eBook
P. 218
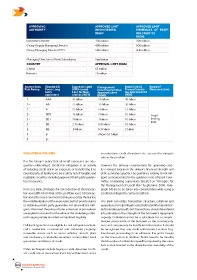
APPROVING APPROVED LIMIT APPROVED LIMIT
AUTHORITY (NeW CreDItS) (reNeWaLS OF exISt-
(NgN) INg CreDItS)
(NgN)
Executive Director 150 million 200 million
Group Deputy Managing Director 400 million 500 million
Group Managing Director/CEO 500 million 600 million
Managing Directors of Bank Subsidiaries See Below:
COUNTRY APPROVAL LIMIT (NGN)
Ghana 65 million
Rwanda 20 million
access Bank Standard & Exposure Limit Management Board Credit & Board of
risk rating Poors Long (ORR-based Credit Committee Finance Commit- Directors Limit
term LLL) for New Approval Limit tee Approval Limit
equivalent credits (NGN) (NGN) (NGN)
1 AAA 41 billion 20 billion 40 billion
2+ AA 33 billion 15 billion 30 billion
2 A 25 billion 5 billion 15 billion
2- BBB 16 billion 2 billion 10 billion Legal
3+ BB+ 3 billion 1 billion 10 billion lending
limit
3 BB 1.7 billion 0.8 billion 10 billion
3- BB- .8 billion 0.5 billion 2 billion
4 B Above 0.1 billion
5 B-
COLLATERAL POLICIES securitisation, credit derivatives etc. are used to mitigate
risks in the portfolio.
It is the Group’s policy that all credit exposures are ade-
quately collateralised. Credit risk mitigation is an activity However the primary consideration for approving cred-
of reducing credit risk in an exposure or transferring it to its is hinged largely on the obligor’s financial strength and
counterparty, at facility level, by a safety net of tangible and debt-servicing capacity. The guidelines relating to risk mit-
realizable securities including approved third-party guaran- igant as incorporated in the guidance note of Basel Com-
tees/ insurance. mittee on Banking Supervision (‘BCBS’) on “Principles for
the Management of Credit Risk” (September 2000, Para-
In Access Bank, strategies for risk reduction at the transac- graph 34) are to be taken into consideration while using a
tion level differ from that at the portfolio level. At transac- credit risk mitigant to control credit risk.
tion level, the most common technique used by the Bank is
the collateralization of the exposures, by first priority claims The Bank can utilize transaction structure, collateral and
or obtaining a third party guarantee. For all credit risk miti- guarantees to help mitigate risks (both identified and inher-
gants that meet the policy criteria, a clear set of procedures ent) in individual credits but transactions should be entered
are applied to ensure that the value of the underlying collat- into primarily on the strength of the borrower’s repayment
eral is appropriately recorded and updated regularly. capacity. Collateral cannot be a substitute for a compre-
hensive assessment of the borrower or the counterparty,
Collateral types that are eligible for risk mitigation include: nor can it compensate for insufficient information. It should
cash; residential, commercial and industrial property; be recognized that any credit enforcement actions (e.g.
moveable assets such as motor vehicles, aircraft, plant foreclosure proceedings) can eliminate the profit margin
and machinery; marketable securities; commodities; bank on the transaction. In addition, Banks need to be mindful
guarantees and letters of credit. that the value of collateral may well be impaired by the same
factors that have led to the diminished recoverability of the
Other techniques include buying a credit derivative to off- credit.
set credit risk at transaction level. At portfolio level, asset
218 Access BAnk Plc
Annual Report & Accounts 2017