Page 11 - MSK assignment
P. 11
11 F. Elahi
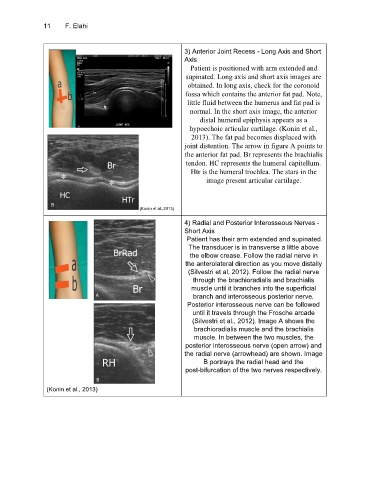
3) Anterior Joint Recess - Long Axis and Short
Axis
Patient is positioned with arm extended and
supinated. Long axis and short axis images are
obtained. In long axis, check for the coronoid
fossa which contains the anterior fat pad. Note,
little fluid between the humerus and fat pad is
normal. In the short axis image, the anterior
distal humeral epiphysis appears as a
hypoechoic articular cartilage. (Konin et al.,
2013). The fat pad becomes displaced with
joint distention. The arrow in figure A points to
the anterior fat pad. Br represents the brachialis
tendon. HC represents the humeral capitellum.
Htr is the humeral trochlea. The stars in the
image present articular cartilage.
(Konin et al.,2013)
4) Radial and Posterior Interosseous Nerves -
Short Axis
Patient has their arm extended and supinated.
The transducer is in transverse a little above
the elbow crease. Follow the radial nerve in
the anterolateral direction as you move distally
(Silvestri et al, 2012). Follow the radial nerve
through the brachioradialis and brachialis
muscle until it branches into the superficial
branch and interosseous posterior nerve.
Posterior interosseous nerve can be followed
until it travels through the Frosche arcade
(Silvestri et al., 2012). Image A shows the
brachioradialis muscle and the brachialis
muscle. In between the two muscles, the
posterior interosseous nerve (open arrow) and
the radial nerve (arrowhead) are shown. Image
B portrays the radial head and the
post-bifurcation of the two nerves respectively.
(Konin et al., 2013)