Page 12 - MSK assignment
P. 12
12 F. Elahi
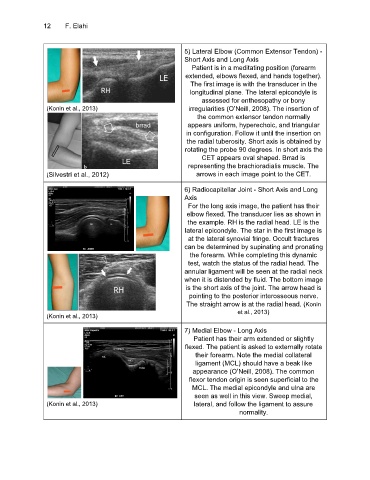
5) Lateral Elbow (Common Extensor Tendon) -
Short Axis and Long Axis
Patient is in a meditating position (forearm
extended, elbows flexed, and hands together).
The first image is with the transducer in the
longitudinal plane. The lateral epicondyle is
assessed for enthesopathy or bony
(Konin et al., 2013) irregularities (O’Neill, 2008). The insertion of
the common extensor tendon normally
appears uniform, hyperechoic, and triangular
in configuration. Follow it until the insertion on
the radial tuberosity. Short axis is obtained by
rotating the probe 90 degrees. In short axis the
CET appears oval shaped. Brrad is
representing the brachioradialis muscle. The
(Silvestri et al., 2012) arrows in each image point to the CET.
6) Radiocapitellar Joint - Short Axis and Long
Axis
For the long axis image, the patient has their
elbow flexed. The transducer lies as shown in
the example. RH is the radial head. LE is the
lateral epicondyle. The star in the first image is
at the lateral synovial fringe. Occult fractures
can be determined by supinating and pronating
the forearm. While completing this dynamic
test, watch the status of the radial head. The
annular ligament will be seen at the radial neck
when it is distended by fluid. The bottom image
is the short axis of the joint. The arrow head is
pointing to the posterior interosseous nerve.
The straight arrow is at the radial head. (Konin
et al., 2013)
(Konin et al., 2013)
7) Medial Elbow - Long Axis
Patient has their arm extended or slightly
flexed. The patient is asked to externally rotate
their forearm. Note the medial collateral
ligament (MCL) should have a beak like
appearance (O’Neill, 2008). The common
flexor tendon origin is seen superficial to the
MCL. The medial epicondyle and ulna are
seen as well in this view. Sweep medial,
(Konin et al., 2013) lateral, and follow the ligament to assure
normality.