Page 13 - MSK assignment
P. 13
13 F. Elahi
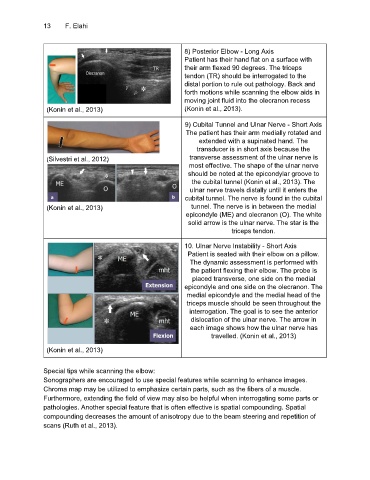
8) Posterior Elbow - Long Axis
Patient has their hand flat on a surface with
their arm flexed 90 degrees. The triceps
tendon (TR) should be interrogated to the
distal portion to rule out pathology. Back and
forth motions while scanning the elbow aids in
moving joint fluid into the olecranon recess
(Konin et al., 2013) (Konin et al., 2013).
9) Cubital Tunnel and Ulnar Nerve - Short Axis
The patient has their arm medially rotated and
extended with a supinated hand. The
transducer is in short axis because the
(Silvestri et al., 2012) transverse assessment of the ulnar nerve is
most effective. The shape of the ulnar nerve
should be noted at the epicondylar groove to
the cubital tunnel (Konin et al., 2013). The
ulnar nerve travels distally until it enters the
cubital tunnel. The nerve is found in the cubital
(Konin et al., 2013) tunnel. The nerve is in between the medial
epicondyle (ME) and olecranon (O). The white
solid arrow is the ulnar nerve. The star is the
triceps tendon.
10. Ulnar Nerve Instability - Short Axis
Patient is seated with their elbow on a pillow.
The dynamic assessment is performed with
the patient flexing their elbow. The probe is
placed transverse, one side on the medial
epicondyle and one side on the olecranon. The
medial epicondyle and the medial head of the
triceps muscle should be seen throughout the
interrogation. The goal is to see the anterior
dislocation of the ulnar nerve. The arrow in
each image shows how the ulnar nerve has
travelled. (Konin et al., 2013)
(Konin et al., 2013)
Special tips while scanning the elbow:
Sonographers are encouraged to use special features while scanning to enhance images.
Chroma map may be utilized to emphasize certain parts, such as the fibers of a muscle.
Furthermore, extending the field of view may also be helpful when interrogating some parts or
pathologies. Another special feature that is often effective is spatial compounding. Spatial
compounding decreases the amount of anisotropy due to the beam steering and repetition of
scans (Ruth et al., 2013).