Page 104 - SAPEM-Chapter-10-2nd-edition-2014
P. 104
South African Pavement Engineering Manual
Chapter 10: Pavement Design
showing that when an asphalt surfacing thicker than 50 mm is used, the asphalt layer contribution to the PN seems
unreasonably high, resulting in an unconservative pavement life. Until data from pavements with asphalt layers
thicker than 50 mm can be obtained, it is not advised to use the PN method for such thick asphalt layers. In the
interim, to obtain reasonable answers, limit the asphalt thickness to 50 mm or less. With thicknesses less than 50
mm, the layer contributions from all the layers seem to balance out to provide reasonable answers.
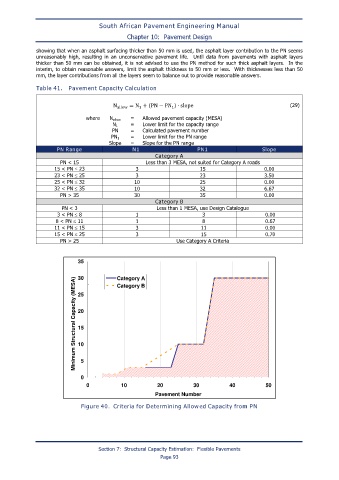
Table 41. Pavement Capacity Calculation
N allow = N + (PN − PN ) ∙ slope (29)
1
1
where N allow = Allowed pavement capacity (MESA)
N 1 = Lower limit for the capacity range
PN = Calculated pavement number
PN 1 = Lower limit for the PN range
Slope = Slope for the PN range
PN Range N1 PN1 Slope
Category A
PN < 15 Less than 3 MESA, not suited for Category A roads
15 < PN ≤ 23 3 15 0.00
23 < PN ≤ 25 3 23 3.50
25 < PN ≤ 32 10 25 0.00
32 < PN ≤ 35 10 32 6.67
PN > 35 30 35 0.00
Category B
PN < 3 Less than 1 MESA, use Design Catalogue
3 < PN ≤ 8 1 3 0.00
8 < PN ≤ 11 1 8 0.67
11 < PN ≤ 15 3 11 0.00
15 < PN ≤ 25 3 15 0.70
PN > 25 Use Category A Criteria
35
Minimum Structural Capacity (MESA) h
30 Category A
Category B
25
20
15
10
5
0
0 10 20 30 40 50
Pavement Number
Figure 40. Criteria for Determining Allowed Capacity from PN
Section 7: Structural Capacity Estimation: Flexible Pavements
Page 93