Page 127 - SAPEM-Chapter-10-2nd-edition-2014
P. 127
South African Pavement Engineering Manual
Chapter 10: Pavement Design
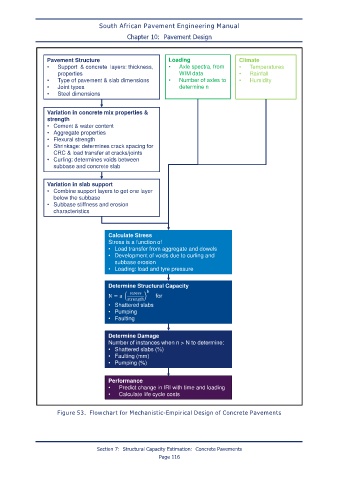
Pavement Structure Loading Climate
• Support & concrete layers: thickness, • Axle spectra, from • Temperatures
properties WIM data • Rainfall
• Type of pavement & slab dimensions • Number of axles to • Humidity
• Joint types determine n
• Steel dimensions
Variation in concrete mix properties &
strength
• Cement & water content
• Aggregate properties
• Flexural strength
• Shrinkage: determines crack spacing for
CRC & load transfer at cracks/joints
• Curling: determines voids between
subbase and concrete slab
Variation in slab support
• Combine support layers to get one layer
below the subbase
• Subbase stiffness and erosion
characteristics
Calculate Stress
Stress is a function of
• Load transfer from aggregate and dowels
• Development of voids due to curling and
subbase erosion
• Loading: load and tyre pressure
Determine Structural Capacity
for
• Shattered slabs
• Pumping
• Faulting
Determine Damage
Number of instances when n > N to determine:
• Shattered slabs (%)
• Faulting (mm)
• Pumping (%)
Performance
• Predict change in IRI with time and loading
• Calculate life cycle costs
Figure 53. Flowchart for Mechanistic-Empirical Design of Concrete Pavements
Section 7: Structural Capacity Estimation: Concrete Pavements
Page 116