Page 358 - 1 Persian Trade rep Bahrain 1_Neat
P. 358
\
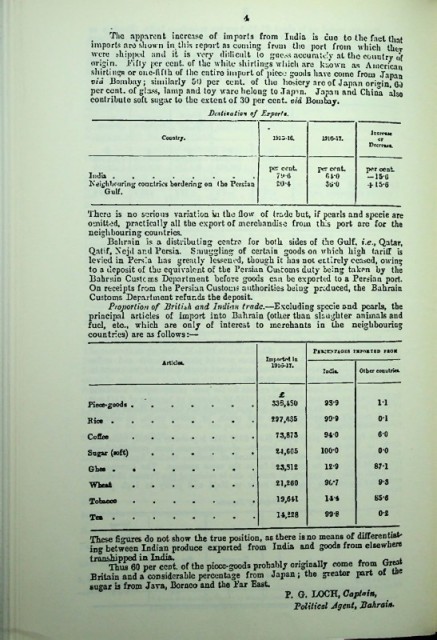
The apparent, increase of imports from India is cue to the fact that
imports arc shown in this report ns coining from the port from which they
were flipped and it is very dillicult to guess accurately at the country of
origin. J/ifty per cent, of the white shirtings which arc known as American
shirtings or onc-fifill of the entire import of piece goods have come from Japan
via Bombay; similarly 50 per cent, of the hosiery arc of Japan origin, 60
per cent, of glass, lamp and toy ware belong to Japan. Japan and China also
contribute soft sugar to the extent of 30 per cent, via Bombay.
Destination of Export*.
IrercTUfl
Countr/. 1515-16. 1516-17. or
Decrease.
per cent. jht cent. per cent
India ........ 7&»*6 61-0 —15-G
Neighbouring coactrios bordering on (ho Persian *20-4 360 + 15-6
Gulf.
There is no serious variation vi the flow of trade but, if pearls and specie are
omitted, practically all the export of merchandise from tins port are for the
neighbouring countries.
Bahrain is a distributing centre for both sides of the Gulf, i.e., Qatar,
Qatif, Xcjd and Persia. Smuggling of certain goods on which high tariff is
levied in Persia lias greatly lessened, though it has not entirely ceased, owing
to a deposit of the equivalent of the Persian Customs duty being taken by the
Bahrain Customs Department before goods can be exported to a Persian port.
On receipts from the Persian Customs authorities beiug produced, the Bahrain
Customs Department refunds the deposit.
Proportion of British and Indian trade.—Excluding specie and pearls, the
principal articles of import into Bahrain (other than slaughter animals and
fuel, etc., which are only of interest to merchants in the neighbouring
countries) are as follows:—
Ps*Ct>TAOE8 TXrOKTED FBOX
Imported in
Articles.
1916-17.
lodls. Other couutrieL
£
Piece-goods . 333,4S0 93*9 11
Bice • 297,635 99*9 01
Coffee 73,873 940 6*0
Sugar (soft) 24,605 100*0 00
Ghee • 23,512 12*9 87*1
Wheat 21,260 9C-7 9*3
Tobacco 19,641 144 85*6
Tea . 14,228 99*8 0*2
These figures do not show the true position, as there is no means of differentiat
ing between Indian produce exported from India and goods from elsewhere
transhipped in India. .
Thus 60 per ccDt. of the piece-goods probably originally come from Great
Britain and a considerable percentage from Japan; the greater part of
sugar is from Java, Borneo and the Par East.
P. G. LOCH, Captain,
Political Agent, Bahrain.
4 4
d