Page 16 - The World About Us
P. 16
Serengeti
1.1.1
2.1.2
What is the distribution of the tropical grasslands?
fig.40 The lt of the earth and
the movement of the ITCZ.
(not drawn to scale)
Approximate posi on of
ITCZ and low pressure
associated with
Tropic of 23.5 N convec onal rainfall.
Cancer
0
Equator 23.5 S
22nd September Equinox
The Sun is overhead at the
Equator bringing low pressure
Tropic of and rain to the Equatorial regions.
Capricorn
Rains move southwards
bringing the dry season
Tropical grasslands Temperate grasslands
to the northern grasslands
fig.39 The global distribu on of tropical and temperate grasslands.
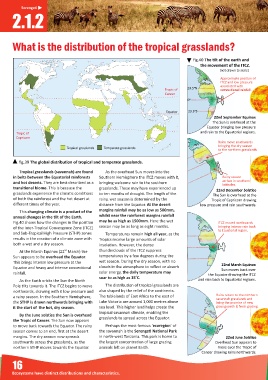
Tropical grasslands (savannah) are found As the overhead Sun moves into the
in belts between the Equatorial rainforests Southern Hemisphere the ITCZ moves with it, Rainy season
and hot deserts. They are best described as a bringing welcome rain to the southern arrives in southern
la tudes.
transi onal biome. This is because the grasslands. These may have experienced up 22nd December Sols ce
grasslands experience the clima c condi ons to ten months of drought. The length of the The Sun is overhead at the
of both the rainforest and the hot desert at rainy, wet season is determined by the Tropic of Capricorn drawing
different mes of the year. distance from the Equator. At the desert low pressure and rain southwards.
margins rainfall may be as low as 500mm,
This changing climate is a product of the
whilst near the rainforest margins rainfall
annual changes in the lt of the Earth.
Fig.40 shows how the changes in the posi on may be as high as 1500mm. Here the wet ITCZ moved northwards
of the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) season may be as long as eight months. bringing intense rain back
to Equatorial region.
and Sub-Tropical High Pressure (STHP) zones Temperatures remain high all year, as the
results in the crea on of a climate zone with Tropics receive large amounts of solar
both a wet and a dry season. insola on. However, the dense
nd
At the March Equinox (22 March) the thunderclouds of the ITCZ suppress
Sun appears to be overhead the Equator. temperatures by a few degrees during the
This brings intense low pressure at the wet season. During the dry season, with no 22nd March Equinox
Equator and heavy and intense convec onal clouds in the atmosphere to reflect or absorb Sun moves back over
rainfall. solar energy, the daily temperature may the Equator drawing the ITCZ
o
soar to as high as 35 C.
As the Earth orbits the Sun the North and rain back to Equatorial regions.
Pole lts towards it. The ITCZ begins to move The distribu on of tropical grasslands are
northwards, drawing with it low pressure and also shaped by the relief of the con nents.
a rainy season. In the Southern Hemisphere, The tablelands of East Africa to the east of Rains return to the northern
savannah grasslands and
the STHP is drawn northwards bringing with Lake Victoria are around 1,000 metres above bring the promise of new
it the start of the hot, dry season. sea level. This higher land helps create the grass growth & fresh grazing.
tropical savannah climate, enabling the
By the June sols ce the Sun is overhead
grasslands to spread across the Equator.
the Tropic of Cancer. The Sun now appears
to move back towards the Equator. The rainy Perhaps the most famous ‘ecoregion’ of
season comes to an end, first at the desert the savannah is the Serenge Na onal Park
margins. The dry season now spreads in north-west Tanzania. This park is home to 22nd June Sols ce
southwards across the grasslands, as the the largest concentra on of large grazing Overhead Sun appears to
northern STHP moves towards the Equator. animals le on planet Earth. move over the Tropic of
Cancer drawing rains northwards.
16
Ecosystems have distinct distributions and characteristics.