Page 4 - The World About Us
P. 4
Chapparal
1.1.1
2.1.1
What are the features of an ecosystem?
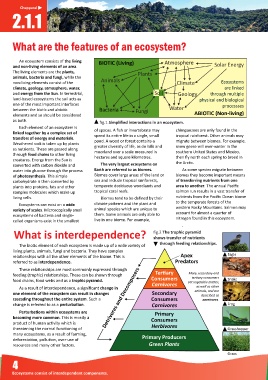
An ecosystem consists of the living BIOTIC (Living) Atmosphere
and non-living elements of an area. Solar Energy
The living elements are the plants, Plants
animals, bacteria and fungi, while the Animals
non-living elements consist of the Climate Ecosystems
climate, geology, atmosphere, water, are linked
and energy from the Sun. In terrestrial, Soil Geology through multiple
land-based ecosystems the soil acts as physical and biological
one of the most important interfaces processses
between the bio c and abio c Bacteria Fungi Water
elements and so should be considered ABIOTIC (Non-living)
as both.
fig.1 Simplified interactions in an ecosystem.
Each element of an ecosystem is
of spaces. A fish or invertebrate may chimpanzees are only found in the
linked together by a complex set of
spend its en re life in a single, small tropical rainforest. Other animals may
transfers of energy and materials.
pond. A wood or forest contains a migrate between biomes. For example,
Weathered rock is taken up by plants
greater diversity of life, as do hills and snow geese will over-winter in the
as nutrients. These are passed along
moorland over a scale measured in southern United States and Mexico,
through food chains to other living
hectares and square kilometres. then fly north each spring to breed in
creatures. Energy from the Sun is the Arc c.
converted with carbon dioxide and The very largest ecosystems on
water into glucose through the process Earth are referred to as biomes. As some species migrate between
of photosynthesis. This simple Biomes cover large areas of the land or biomes they become important means
carbohydrate is then converted by sea and include tropical rainforests, of transferring nutrients from one
plants into proteins, fats and other temperate deciduous woodlands and area to another. The annual Pacific
complex molecules which make up tropical coral reefs. salmon run results in a vast transfer of
living cells. Biomes tend to be defined by their nutrients from the Pacific Ocean biome
to the temperate forests of the
Ecosystems can exist on a wide climate pa erns and the plant and
variety of scales. Microscopically small animal species which are unique to western Rocky Mountains. Salmon may
account for almost a quarter of
ecosystems of bacteria and single- them. Some animals are only able to nitrogen found in this ecosystem.
celled organisms exist in the smallest live in one biome. For example,
.
What is interdependence? fig.2 The trophic pyramid
shows transfer of nutrients
through feeding relationships.
The bio c element of each ecosystem is made up of a wide variety of
living plants, animals, fungi and bacteria. They have complex
rela onships with all the other elements of the biome. This is Apex Eagle
referred to as interdependence. Predators
These rela onships are most commonly expressed through
feeding (trophic) rela onships. These can be shown through Ter ary Many secondary and
ter ary consumers
food chains, food webs and as a trophic pyramid. Consumers eat vegetable ma er, Snake
Carnivores
As a result of interdependence, a significant change in as well as other
one element of the ecosystem can result in changes Secondary animals, and are
described as
cascading throughout the en re system. Such a Detrivores and Decomposers Consumers omnivores.
change is referred to as a perturba on. Carnivores Frog
Perturba ons within ecosystems are Primary
becoming more common. This is mostly a Consumers
product of human ac vity which is Herbivores
threatening the normal func oning of Grasshopper
many ecosystems, as a result of farming, Primary Producers
deforesta on, pollu on, over-use of
resources and many other factors. Green Plants
Grass
4
Ecosystems consist of interdependent components.