Page 316 - NEWNORMAL_ANIMATED
P. 316
NEW NORMAL
We will now analyze the individual catego- the government or law in your country - the
ries listed in the general calculation formula in important thing is for how long you will use it
more detail. The specificity of wine production before you buy a new one.
is the fact that grape production is an agricul- The depreciation of all machinery, equip-
tural process and wine production is a classic ment and facilities used for the production of
non-agricultural, i.e. production process. So, grapes or wine is calculated in a similar way. If
there are basically two price calculations - the the technical device is also used for other pur-
calculation of the price of grapes as the final poses, only a proportion of the depreciation of
product of agricultural activity and the calcu- the device is included in the amount of depre-
lation of the price of wine as such. ciation - typically for means of transport such
as vans. By adding up the depreciation, we
CALCULATION OF THE COST PRICE OF obtain the sum of depreciation, which will be
GRAPES part of the production overheads according to
So, what is calculated when it comes to the the general calculation formula.
price of grapes? The price of grapes includes
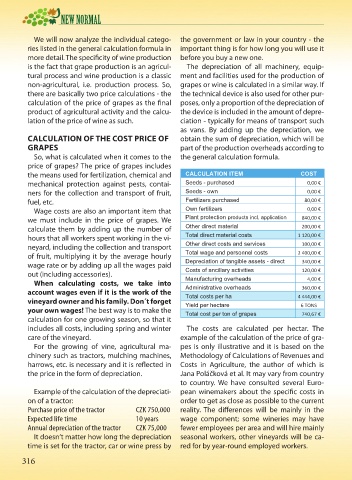
the means used for fertilization, chemical and &$/&8/$7,21 ,7(0 &267
mechanical protection against pests, contai- 6HHGV SXUFKDVHG Ϭ͕ϬϬ Φ
ners for the collection and transport of fruit, 6HHGV RZQ Ϭ͕ϬϬ Φ
)HUWLOL]HUV SXUFKDVHG ϴϬ͕ϬϬ Φ
fuel, etc.
2ZQ IHUWLOL]HUV Ϭ͕ϬϬ Φ
Wage costs are also an important item that
3ODQW SURWHFWLRQ SURGXFWV LQFO DSSOLFDWLRQ ϴϰϬ͕ϬϬ Φ
we must include in the price of grapes. We
2WKHU GLUHFW PDWHULDO ϮϬϬ͕ϬϬ Φ
calculate them by adding up the number of
7RWDO GLUHFW PDWHULDO FRVWV ϭ ϭϮϬ͕ϬϬ Φ
hours that all workers spent working in the vi-
2WKHU GLUHFW FRVWV DQG VHUYLFHV ϭϬϬ͕ϬϬ Φ
neyard, including the collection and transport
7RWDO ZDJH DQG SHUVRQQHO FRVWV Ϯ ϰϬϬ͕ϬϬ Φ
of fruit, multiplying it by the average hourly
'HSUHFLDWLRQ RI WDQJLEOH DVVHWV GLUHFW ϯϰϬ͕ϬϬ Φ
wage rate or by adding up all the wages paid
&RVWV RI DQFLOODU\ DFWLYLWLHV ϭϮϬ͕ϬϬ Φ
out (including accessories).
0DQXIDFWXULQJ RYHUKHDGV ϰ͕ϬϬ Φ
When calculating costs, we take into
$GPLQLVWUDWLYH RYHUKHDGV ϯϲϬ͕ϬϬ Φ
account wages even if it is the work of the
7RWDO FRVWV SHU KD ϰ ϰϰϰ͕ϬϬ Φ
vineyard owner and his family. Don´t forget
<LHOG SHU KHFWDUH ϲ dKE^
your own wages! The best way is to make the
7RWDO FRVW SHU WRQ RI JUDSHV ϳϰϬ͕ϲϳ Φ
calculation for one growing season, so that it
includes all costs, including spring and winter The costs are calculated per hectar. The
care of the vineyard. example of the calculation of the price of gra-
For the growing of vine, agricultural ma- pes is only illustrative and it is based on the
chinery such as tractors, mulching machines, Methodology of Calculations of Revenues and
harrows, etc. is necessary and it is reflected in Costs in Agriculture, the author of which is
the price in the form of depreciation. Jana Poláčková et al. It may vary from country
to country. We have consulted several Euro-
Example of the calculation of the depreciati- pean winemakers about the specific costs in
on of a tractor: order to get as close as possible to the current
Purchase price of the tractor CZK 750,000 reality. The differences will be mainly in the
Expected life time 10 years wage component; some wineries may have
Annual depreciation of the tractor CZK 75,000 fewer employees per area and will hire mainly
It doesn‘t matter how long the depreciation seasonal workers, other vineyards will be ca-
time is set for the tractor, car or wine press by red for by year-round employed workers.
316