Page 27 - AAS & AES & FES 01082016_Neat
P. 27
e e
energies and consequently are more likely to be ionized at the temperatures of most AAS cells nergies and consequently are more likely to be ionized at the temperatures of most AAS cells nergies and consequently are more likely to be ionized at the temperatures of most AAS cells
than other elements.
Ionization is dependent upon concentration. Generally as the concentration of an element onization is dependent upon concentration. Generally as the concentration of an element onization is dependent upon concentration. Generally as the concentration of an element
I I
increases, the relative amount of ionization of the element decreases. Apparently that is the result ases, the relative amount of ionization of the element decreases. Apparently that is the result ases, the relative amount of ionization of the element decreases. Apparently that is the result
o o
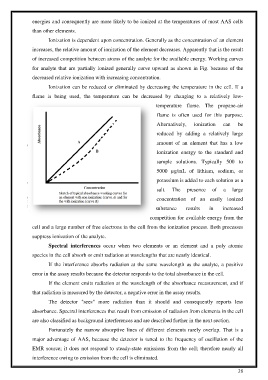
of increased competition between atoms of the analyte for the available energy. Working curves f increased competition between atoms of the analyte for the available energy. Working curves f increased competition between atoms of the analyte for the available energy. Working curves
f for analyte that are partially ionized generally curve upward as or analyte that are partially ionized generally curve upward as shown in Fig. because of the shown in Fig. because of the
decreased relative ionization with increasing concentration. ecreased relative ionization with increasing concentration.
d
I I
Ionization can be reduced or eliminated by decreasing the temperature in the cell. If a onization can be reduced or eliminated by decreasing the temperature in the cell. If a onization can be reduced or eliminated by decreasing the temperature in the cell. If a
f f flame is being used, the temperature can be decreased by changing to a relatlame is being used, the temperature can be decreased by changing to a relatlame is being used, the temperature can be decreased by changing to a relatively low-
t
temperature flame. The propaneemperature flame. The propane-air
f
flame is often used for thislame is often used for this purpose.
i
Alternatively, lternatively, ionization onization c b
be e
A
can an
r
reduced by adding a relatively large educed by adding a relatively large
a
amount of an element that has a low mount of an element that has a low
I Ionization energy to the standard and onization energy to the standard and
sample solutions. Typically 5ample solutions. Typically 500 to
s
5
5000 µg/mL of lithium, sodium, or 000 µg/mL of lithium, sodium, or
potassium is added to each solution as a otassium is added to each solution as a
p
salt. The presence of a large alt. The presence of a large
s
c
concentration of an easily ionized oncentration of an easily ionized
s
substance ubstance results esults i in n increased ncreased
r
i
c
competition for available energy from the ompetition for available energy from the
cell and a large number of free electell and a large number of free electrons in the cell from the ionization process. Both processes rons in the cell from the ionization process. Both processes
c
s
suppress ionization of the analyte.uppress ionization of the analyte.
S
Spectral interferencespectral interferences occur when two elements or an element and a poly ments or an element and a poly atomic
s
species in the cell absorb or emit radiation at wavelengths pecies in the cell absorb or emit radiation at wavelengths that are nearly identical. identical.
If the interference absorbs radiation af the interference absorbs radiation at the same wavelength as thethe same wavelength as the analyte, a positive
I
error in the assay results because the detector responds to theassay results because the detector responds to the total absorbanceance in the cell.
I
If the element emits radiation at the wavelength f the element emits radiation at the wavelength of the absorbance measurement, and if bance measurement, and if
t that radiation is measured by the detectorhat radiation is measured by the detector, a negative error in the assay results.ive error in the assay results.
T
The detector "sees" more radiation than he detector "sees" more radiation than it should and consequently reports less hould and consequently reports less
absorbance. Spectral interferencesinterferences that result from emission of radiation from elements in the cell result from emission of radiation from elements in the cell
are also classified as background interferences and are described further in the next section.background interferences and are described further in the next section.background interferences and are described further in the next section.
F F
Fortunately the narrow absorptive lines of different elements rarely ortunately the narrow absorptive lines of different elements rarely ortunately the narrow absorptive lines of different elements rarely overlap. That is a
major advantage of AAS, becausebecause the detector is tuned to the frequencyuency of oscillation of the
EMR source; it does not respond to steadyMR source; it does not respond to steady-state emissions from the celfrom the cell; therefore nearly all
E
i
interference owing to emission from the celnterference owing to emission from the cell is eliminated.
26