Page 49 - Proceeding of Atrans Young Researcher's Forum 2019_Neat
P. 49
“Transportation for A Better Life:
Smart Mobility for Now and Then”
23 August 2019, Bangkok, Thailand
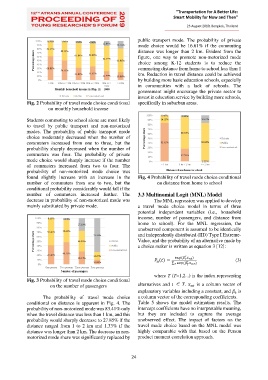
public transport mode. The probability of private
mode choice would be 16.61% if the commuting
distance was longer than 2 km. Evident from the
figure, one way to promote non-motorized mode
choice among K-12 students is to reduce the
commuting distance from home to school less than 1
km. Reduction in travel distance could be achieved
by building more basic education schools, especially
in communities with a lack of schools. The
government might encourage the private sector to
invest in education service by building more schools,
Fig. 2 Probability of travel mode choice conditional specifically in suburban areas.
on monthly household income
Students commuting to school alone are most likely
to travel by public transport and non-motorized
modes. The probability of public transport mode
choice moderately decreased when the number of
commuters increased from one to three, but the
probability sharply decreased when the number of
commuters was four. The probability of private
mode choice would sharply increase if the number
of commuters increased from two to four. The
probability of non-motorized mode choice was
found slightly increase with an increase in the Fig. 4 Probability of travel mode choice conditional
number of commuters from one to two, but the on distance from home to school
conditional probability considerably would fall if the
number of commuters increased further. The 3.3 Multinomial Logit (MNL) Model
decrease in probability of non-motorized mode was The MNL regression was applied to develop
mainly substituted by private mode. a travel mode choice model in terms of three
potential independent variables (i.e., household
income, number of passengers, and distance from
home to school). For the MNL regression, the
unobserved component is assumed to be identically
and independently distributed (IID) Type I Extreme-
Value, and the probability of an alternative made by
a choice maker is written as equation 3 [12]:
′
exp ( )
() = ∑ exp ( ) (3)
′
where T (T=1,2…) is the index representing
Fig. 3 Probability of travel mode choice conditional
on the number of passengers alternatives and t ∈ T. is a column vector of
explanatory variables including a constant, and is
The probability of travel mode choice a column vector of the corresponding coefficients.
conditional on distance is apparent in Fig. 4. The Table 5 shows the model estimation results. The
probability of non-motorized mode was 83.41% only intercept coefficients have no interpretable meaning,
when the travel distance was less than 1 km, and this but they are included to capture the average
probability would sharply decrease to 27.85% if the unobserved effect. The impact of factors on the
distance ranged from 1 to 2 km and 1.33% if the travel mode choice based on the MNL model was
distance was longer than 2 km. The decrease in non- highly comparable with that based on the Person
motorized mode share was significantly replaced by product moment correlation approach.
24