Page 39 - OF0620 Online_Neat
P. 39
Quality & nutrition
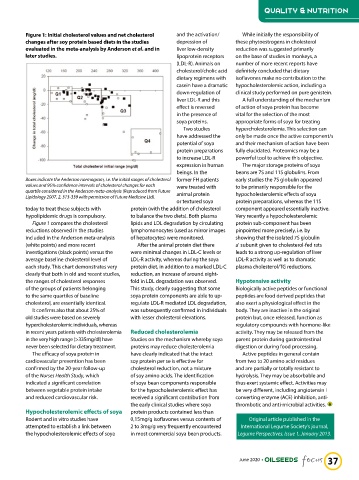
Figure 1: Initial cholesterol values and net cholesterol and the activation/ While initially the responsibility of
changes after soy protein based diets in the studies depression of these phytoestrogens in cholesterol
evaluated in the meta-analysis by Anderson et al. and in liver low-density reduction was suggested primarily
later studies. lipoprotein receptors on the base of studies in monkeys, a
(LDL-R). Animals on number of more recent reports have
cholesterol/cholic acid definitely concluded that dietary
dietary regimens with isoflavones make no contribution to the
casein have a dramatic hypocholesterolemic action, including a
down-regulation of clinical study performed on pure genistein.
liver LDL-R and this A full understanding of the mechanism
effect is reversed of action of soya protein has become
in the presence of vital for the selection of the most
soya proteins. appropriate forms of soya for treating
Two studies hypercholesterolemia. This selection can
have addressed the only be made once the active component/s
potential of soya and their mechanism of action have been
protein preparations fully elucidated. Proteomics may be a
to increase LDL-R powerful tool to achieve this objective.
expression in human The major storage proteins of soya
beings. In the beans are 7S and 11S globulins. From
Boxes indicate the Anderson normogram, i.e. the initial ranges of cholesterol former FH patients early studies the 7S globulin appeared
values and 95% confidence intervals of cholesterol changes for each were treated with to be primarily responsible for the
quartile considered in the Anderson meta-analysis (Reproduced from Future animal protein hypocholesterolemic effects of soya
Lipidology 2007, 2, 313-339 with permission of Future Medicine Ltd).
or textured soya protein preparations, whereas the 11S
today to treat these subjects with protein (with the addition of cholesterol component appeared essentially inactive.
hypolipidemic drugs is compulsory. to balance the two diets). Both plasma Very recently a hypocholesterolemic
Figure 1 compares the cholesterol lipids and LDL degradation by circulating protein sub-component has been
reductions observed in the studies lymphomonocytes (used as mirror images pinpointed more precisely, i.e. by
included in the Anderson meta-analysis of hepatocytes) were monitored. showing that the isolated 7S globulin
(white points) and more recent After the animal protein diet there a‘ subunit given to cholesterol-fed rats
investigations (black points) versus the were minimal changes in LDL-C levels or leads to a strong up-regulation of liver
average baseline cholesterol level of LDL-R activity, whereas during the soya LDL-R activity as well as to dramatic
each study. This chart demonstrates very protein diet, in addition to a marked LDL-C plasma cholesterol/TG reductions.
clearly that both in old and recent studies, reduction, an increase of around eight-
the ranges of cholesterol responses fold in LDL degradation was observed. Hypotensive activity
of the groups of patients belonging This study, clearly suggesting that some Biologically active peptides or functional
to the same quartiles of baseline soya protein components are able to up- peptides are food derived peptides that
cholesterol, are essentially identical. regulate LDL-R mediated LDL degradation, also exert a physiological effect in the
It confirms also that about 25% of was subsequently confirmed in individuals body. They are inactive in the original
old studies were based on severely with lesser cholesterol elevations. protein but, once released, function as
hypercholesterolemic individuals, whereas regulatory compounds with hormone-like
in recent years patients with cholesterolemia Reduced cholesterolemia activity. They may be released from the
in the very high range (>335mg/dl) have Studies on the mechanism whereby soya parent protein during gastrointestinal
never been selected for dietary treatment. proteins may reduce cholesterolemia digestion or during food processing.
The efficacy of soya protein in have clearly indicated that the intact Active peptides in general contain
cardiovascular prevention has been soy protein per se is effective for from two to 20 amino acid residues
confirmed by the 20-year follow-up cholesterol reduction, not a mixture and are partially or totally resistant to
of the Nurses Health Study, which of soy amino acids. The identification hydrolysis. They may be absorbable and
indicated a significant correlation of soya bean components responsible thus exert systemic effect. Activities may
between vegetable protein intake for the hypocholesterolemic effect has be very different, including angiotensin I
and reduced cardiovascular risk. received a significant contribution from converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition, anti-
the early clinical studies where soya thrombotic and anti-microbial activities.
Hypocholesterolemic effects of soya protein products contained less than
Rodent and in vitro studies have 0,15mg/g isoflavones versus contents of Original article published in the
attempted to establish a link between 2 to 3mg/g very frequently encountered International Legume Society’s journal,
the hypocholesterolemic effects of soya in most commercial soya bean products. Legume Perspectives, Issue 1, January 2013.
June 2020 37