Page 43 - OF0620 Online_Neat
P. 43
Quality & nutrition
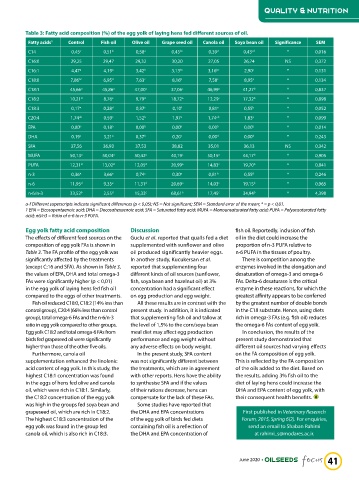
Table 3: Fatty acid composition (%) of the egg yolk of laying hens fed different sources of oil.
Fatty acids 1 Control Fish oil Olive oil Grape seed oil Canola oil Soya bean oil Significance SEM
C14 0,45 c 0,51 b 0,58 a 0,45 bc 0,39 d 0,43 cd * 0,016
C16:0 29,25 29,47 29,32 30,20 27,05 26,74 NS 0,372
C16:1 4,47 a 4,19 a 3,42 b 3,13 bc 3,16 bc 2,90 c * 0,131
C18:0 7,86 bc 6,95 d 7,63 c 8,16 b 7,58 c 8,95 a * 0,134
C18:1 45,66 a 45,86 a 47,00 a 37,06 c 46,99 a 41,27 b * 0,837
C18:2 10,21 d 8,76 e 9,79 d 18,72 a 12,29 c 17,32 b * 0,898
C18:3 0,17 e 0,28 d 0,37 c 0,10 f 0,81 a 0,55 b * 0,052
C20:4 1,74 ab 0,59 c 1,52 b 1,97 a 1,74 ab 1,83 a * 0,099
EPA 0,00 b 0,18 a 0,00 b 0,00 b 0,00 b 0,00 b * 0,014
DHA 0,19 c 3,21 a 0,37 b 0,20 c 0,00 d 0,00 d * 0,243
SFA 37,56 36,93 37,53 38,82 35,01 36,13 NS 0,342
MUFA 50,13 a 50,04 a 50,42 a 40,19 c 50,15 a 44,17 b * 0,905
PUFA 12,31 d 13,02 d 12,05 d 20,99 a 14,83 c 19,70 b * 0,841
n-3 0,36 e 3,66 a 0,74 c 0,30 e 0,81 b 0,55 d * 0,246
n-6 11,95 d 9,35 e 11,31 d 20,69 a 14,03 c 19,15 b * 0,965
n-6/n-3 33,52 b 2,55 d 15,33 c 68,61 a 17,45 c 34,94 b * 4,398
a-f Different superscripts indicate significant differences (p < 0,05); NS = Not significant; SEM = Standard error of the mean; * = p < 0,01.
1 EPA = Eicosapentaenoic acid; DHA = Docosahexaenoic acid; SFA = Saturated fatty acid; MUFA = Monounsaturated fatty acid; PUFA = Polyunsaturated fatty
acid; n6/n3 = Ratio of n-6 to n-3 PUFA.
Egg yolk fatty acid composition Discussion fish oil. Reportedly, inclusion of fish
The effects of different feed sources on the Guclu et al. reported that quails fed a diet oil in the diet could increase the
composition of egg yolk FAs is shown in supplemented with sunflower and olive proportion of n-3 PUFA relative to
Table 3. The FA profile of the egg yolk was oil produced significantly heavier eggs. n-6 PUFA in the tissues of poultry.
significantly affected by the treatments In another study, Kucukersan et al. There is competition among the
(except C:16 and SFA). As shown in Table 3, reported that supplementing four enzymes involved in the elongation and
the values of EPA, DHA and total omega-3 different kinds of oil sources (sunflower, desaturation of omega-3 and omega-6
FAs were significantly higher (p < 0,01) fish, soya bean and hazelnut oil) at 3% FAs. Delta-6 desaturase is the critical
in the egg yolk of laying hens fed fish oil concentration had a significant effect enzyme in these reactions, for which the
compared to the eggs of other treatments. on egg production and egg weight. greatest affinity appears to be conferred
Fish oil reduced C18:0, C18:2 (14% less than All these results are in contrast with the by the greatest number of double bonds
control group), C20:4 (66% less than control present study. In addition, it is indicated in the C18 substrate. Hence, using diets
group), total omega-6 FAs and the n-6/n-3 that supplementing fish oil and tallow at rich in omega-3 FAs (e.g. fish oil) reduces
ratio in egg yolk compared to other groups. the level of 1,5% to the corn/soya bean the omega-6 FAs content of egg yolk.
Egg yolk C18:2 and total omega-6 FAs from meal diet may affect egg production In conclusion, the results of the
birds fed grapeseed oil were significantly performance and egg weight without present study demonstrated that
higher than those of the other five oils. any adverse effects on body weight. different oil sources had varying effects
Furthermore, canola oil In the present study, SFA content on the FA composition of egg yolk.
supplementation enhanced the linolenic was not significantly different between This is reflected by the FA composition
acid content of egg yolk. In this study, the the treatments, which are in agreement of the oils added to the diet. Based on
highest C18:1 concentration was found with other reports. Hens have the ability the results, adding 3% fish oil to the
in the eggs of hens fed olive and canola to synthesise SFA and if the values diet of laying hens could increase the
oil, which were rich in C18:1. Similarly, of their rations decrease, hens can DHA and EPA content of egg yolk, with
the C18:2 concentration of the egg yolk compensate for the lack of these FAs. their consequent health benefits.
was high in the groups fed soya bean and Some studies have reported that
grapeseed oil, which are rich in C18:2. the DHA and EPA concentrations First published in Veterinary Research
The highest C18:3 concentration of the of the egg yolk of birds fed diets Forum, 2015, Spring 6(2). For enquiries,
egg yolk was found in the group fed containing fish oil is a reflection of send an email to Shaban Rahimi
canola oil, which is also rich in C18:3. the DHA and EPA concentration of at rahimi_s@modares.ac.ir.
June 2020 41