Page 33 - Technology Roadmap Transportation
P. 33
TECHNOLOGY ROADMAP: TRANSPORTATION
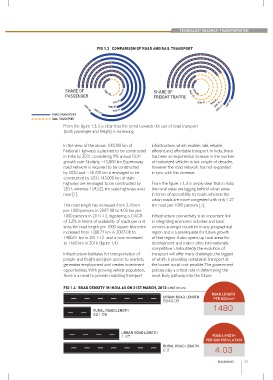
FIG 1.3 COMPARISON OF ROAD AND RAIL TRANSPORT
SHARE OF 1950-51 1960-61 SHARE OF 1960-61
1950-51
PASSENGER FREIGHT TRAFFIC
1970-71 1970-71 1980-81 2007-08
2000-07
1980-81 1990-91
1990-91
2007-08
2000-07
ROAD TRANSPORT
RAIL TRANSPORT
From the figure 1.3, it is clear that the trend towards the use of road transport
(both passenger and freight) is increasing.
In the view of the above, 100,000 km of infrastructure, which enables safe, reliable,
National Highways is planned to be constructed efficient, and affordable transport. In India, there
in India by 2031, considering 9% annual GDP has been an exponential increase in the number
growth rate. Similarly, ~15,800 km Expressway of motorized vehicles in last couple of decades,
road network is required to be constructed however the road network has not expanded
by 2020 and ~18,700 km is envisaged to be in sync with this increase.
constructed by 2031.145,000 km of state
highways are envisaged to be constructed by From the figure 1.4, it is amply clear that in India
2031, whereas 154,522 km state highways exist the rural areas are lagging behind urban areas
now [1]. in terms of accessibility to roads, whereas the
urban roads are more congested with only 1.27
The road length has increased from 3.70 km km road per 1000 persons [7].
per 1000 persons in 2007-08 to 4.03 km per
1000 persons in 2011-12, registering a CAGR Infrastructure connectivity is an important link
of 2.2%. In terms of availability of roads per unit in integrating economic activities and basic
area, the road length per 1000 square kilometre services amongst countries in any geographical
increased from 1288.74 km in 2007-08 to region and is a prerequisite for future growth
1480.07 km in 2011-12 and is now increased of that region. It also opens up rural areas for
to 1660 km in 2016 (figure 1.4). development and makes cities internationally
competitive. Undoubtedly, the evolution of
Infrastructure facilitates for transportation of transport will offer many challenges, the biggest
people and freight and gives access to markets, of which is providing sustainable transport at
generates employment and creates investment the lowest social cost possible. The government
opportunities. With growing vehicle population, policies play a critical role in determining the
there is a need to provide matching transport most likely pathway into the future.
FIG 1.4 ROAD DENSITY IN INDIA AS ON 31ST MARCH, 2012 (UNIT IN km)
ROAD LENGTH
URBAN ROAD LENGTH PER 1000 km 2
5940.05
1480
RURAL ROAD LENGTH
621.58
URBAN ROAD LENGTH
1.27 ROAD LENGTH
PER 1000 POPULATION
RURAL ROAD LENGTH
2.3 4.03
ROADWAYS 31