Page 114 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 114
P1: FAW
BLUK007-03 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 17:29 Char Count= 0
110 Chapter 3: Respiratory system
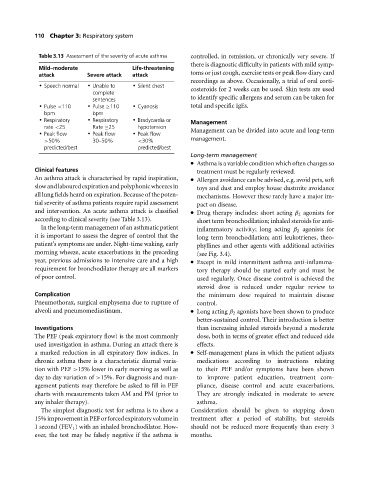
Table 3.13 Assessment of the severity of acute asthma controlled, in remission, or chronically very severe. If
there is diagnostic difficulty in patients with mild symp-
Mild–moderate Life-threatening
attack Severe attack attack toms or just cough, exercise tests or peak flow diary card
recordings as above. Occasionally, a trial of oral corti-
Speech normal Unable to Silent chest costeroids for 2 weeks can be used. Skin tests are used
complete
sentences to identify specific allergens and serum can be taken for
Pulse <110 Pulse ≥110 Cyanosis
total and specific IgEs.
bpm bpm
Respiratory Respiratory Bradycardia or Management
rate <25 Rate ≥25 hypotension
Peak flow Peak flow Peak flow
Management can be divided into acute and long-term
>50% 30–50% <30% management.
predicted/best predicted/best
Long-term management
Asthma is a variable condition which often changes so
Clinical features treatment must be regularly reviewed.
An asthma attack is characterised by rapid inspiration, Allergen avoidance can be advised, e.g. avoid pets, soft
slowandlabouredexpirationandpolyphonicwheezesin toys and dust and employ house dustmite avoidance
all lung fields heard on expiration. Because of the poten- mechanisms. However these rarely have a major im-
tial severity of asthma patients require rapid assessment pact on disease.
and intervention. An acute asthma attack is classified Drug therapy includes: short acting β 2 agonists for
according to clinical severity (see Table 3.13). short term bronchodilation; inhaled steroids for anti-
In the long-term management of an asthmatic patient inflammatory activity; long acting β 2 agonists for
it is important to assess the degree of control that the long term bronchodilation; anti leukotrienes, theo-
patient’s symptoms are under. Night-time waking, early phyllines and other agents with additional activities
morning wheeze, acute exacerbations in the preceding (see Fig. 3.4).
year, previous admissions to intensive care and a high Except in mild intermittent asthma anti-inflamma-
requirement for bronchodilator therapy are all markers tory therapy should be started early and must be
of poor control. used regularly. Once disease control is achieved the
steroid dose is reduced under regular review to
Complication the minimum dose required to maintain disease
Pneumothorax, surgical emphysema due to rupture of control.
alveoli and pneumomediastinum. Long acting β 2 agonists have been shown to produce
better-sustained control. Their introduction is better
Investigations than increasing inhaled steroids beyond a moderate
The PEF (peak expiratory flow) is the most commonly dose, both in terms of greater effect and reduced side
used investigation in asthma. During an attack there is effects.
a marked reduction in all expiratory flow indices. In Self-management plans in which the patient adjusts
chronic asthma there is a characteristic diurnal varia- medications according to instructions relating
tion with PEF >15% lower in early morning as well as to their PEF and/or symptoms have been shown
day to day variation of >15%. For diagnosis and man- to improve patient education, treatment com-
agement patients may therefore be asked to fill in PEF pliance, disease control and acute exacerbations.
charts with measurements taken AM and PM (prior to They are strongly indicated in moderate to severe
any inhaler therapy). asthma.
The simplest diagnostic test for asthma is to show a Consideration should be given to stepping down
15%improvementinPEForforcedexpiratoryvolumein treatment after a period of stability, but steroids
1second (FEV 1 )with an inhaled bronchodilator. How- should not be reduced more frequently than every 3
ever, the test may be falsely negative if the asthma is months.