Page 243 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 243
P1: KPE
BLUK007-06 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 18:6 Char Count= 0
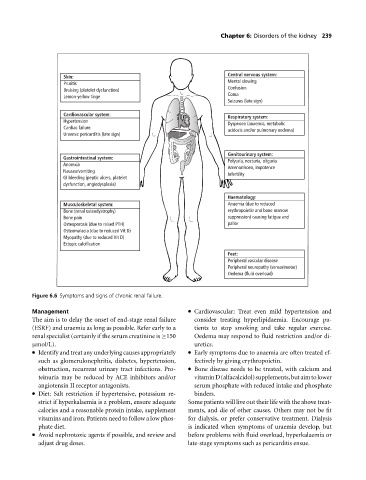
Chapter 6: Disorders of the kidney 239
Central nervous system:
Skin:
Mental slowing
Pruritis
Confusion
Bruising (platelet dysfunction)
Coma
Lemon-yellow tinge
Seizures (late sign)
Cardiovascular system:
Respiratory system:
Hypertension Dyspnoea (anaemia, metabolic
Cardiac failure
acidosis and/or pulmonary oedema)
Uraemic pericarditis (late sign)
Genitourinary system:
Gastrointestinal system:
Polyuria, nocturia, oliguria
Anorexia
Amenorrhoea, impotence
Nausea/vomiting
Infertility
GI bleeding (peptic ulcers, platelet
dysfunction, angiodysplasia)
Haematology:
Musculoskeletal system: Anaemia (due to reduced
Bone (renal osteodystrophy) erythropoietin and bone marrow
Bone pain suppression) causing fatigue and
Osteoporosis (due to raised PTH) pallor
Osteomalacia (due to reduced Vit D)
Myopathy (due to reduced Vit D)
Ectopic calcification
Feet:
Peripheral vascular disease
Peripheral neuropathy (sensorimotor)
Oedema (fluid overload)
Figure 6.6 Symptoms and signs of chronic renal failure.
Management Cardiovascular: Treat even mild hypertension and
The aim is to delay the onset of end-stage renal failure consider treating hyperlipidaemia. Encourage pa-
(ESRF) and uraemia as long as possible. Refer early to a tients to stop smoking and take regular exercise.
renal specialist (certainly if the serum creatinine is ≥150 Oedema may respond to fluid restriction and/or di-
µmol/L). uretics.
Identify and treat any underlying causes appropriately Early symptoms due to anaemia are often treated ef-
such as glomerulonephritis, diabetes, hypertension, fectively by giving erythropoietin.
obstruction, recurrent urinary tract infections. Pro- Bone disease needs to be treated, with calcium and
teinuria may be reduced by ACE inhibitors and/or vitaminD(alfacalcidol)supplements,butaimtolower
angiotensin II receptor antagonists. serum phosphate with reduced intake and phosphate
Diet: Salt restriction if hypertensive, potassium re- binders.
strict if hyperkalaemia is a problem, ensure adequate Some patients will live out their life with the above treat-
calories and a reasonable protein intake, supplement ments, and die of other causes. Others may not be fit
vitamins and iron. Patients need to follow a low phos- for dialysis, or prefer conservative treatment. Dialysis
phate diet. is indicated when symptoms of uraemia develop, but
Avoid nephrotoxic agents if possible, and review and before problems with fluid overload, hyperkalaemia or
adjust drug doses. late-stage symptoms such as pericarditis ensue.