Page 246 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 246
P1: KPE
BLUK007-06 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 18:6 Char Count= 0
242 Chapter 6: Genitourinary system
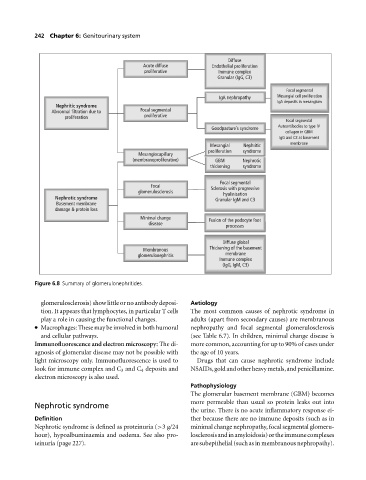
Diffuse
Acute diffuse Endothelial proliferation
proliferative Immune complex
Granular (IgG, C3)
Focal segmental
IgA nephropathy Mesangial cell proliferation
IgA deposits in mesangium
Nephritic syndrome
Abnormal filtration due to Focal segmental
proliferation proliferative
Focal segmental
Autoantibodies to type IV
Goodpasture’s syndrome
collagen in GBM
IgG and C3 at basement
membrane
Mesangial Nephritic
proliferation syndrome
Mesangiocapillary
(membranoproliferative) GBM Nephrotic
thickening syndrome
Focal segmental
Focal Sclerosis with progressive
glomerulosclerosis hyalinisation
Nephrotic syndrome Granular IgM and C3
Basement membrane
damage & protein loss
Minimal change Fusion of the podocyte foot
disease
processes
Diffuse global
Thickening of the basement
Membranous
glomerulonephritis membrane
Immune complex
(IgG, IgM, C3)
Figure 6.8 Summary of glomerulonephritides.
glomerulosclerosis) show little or no antibody deposi- Aetiology
tion. It appears that lymphocytes, in particular T cells The most common causes of nephrotic syndrome in
play a role in causing the functional changes. adults (apart from secondary causes) are membranous
Macrophages: These may be involved in both humoral nephropathy and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
and cellular pathways. (see Table 6.7). In children, minimal change disease is
Immunofluorescence and electron microscopy: The di- more common, accounting for up to 90% of cases under
agnosis of glomerular disease may not be possible with the age of 10 years.
light microscopy only. Immunofluorescence is used to Drugs that can cause nephrotic syndrome include
look for immune complex and C 3 and C 4 deposits and NSAIDs,goldandotherheavymetals,andpenicillamine.
electron microscopy is also used.
Pathophysiology
The glomerular basement membrane (GBM) becomes
more permeable than usual so protein leaks out into
Nephrotic syndrome
the urine. There is no acute inflammatory response ei-
Definition ther because there are no immune deposits (such as in
Nephrotic syndrome is defined as proteinuria (>3 g/24 minimal change nephropathy, focal segmental glomeru-
hour), hypoalbuminaemia and oedema. See also pro- losclerosisandinamyloidosis)ortheimmunecomplexes
teinuria (page 227). are subepithelial (such as in membranous nephropathy).