Page 493 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 493
P1: KOA
BLUK007-12 BLUK007-Kendall May 12, 2005 20:37 Char Count= 0
Chapter 12: Leukaemia and lymphoma 489
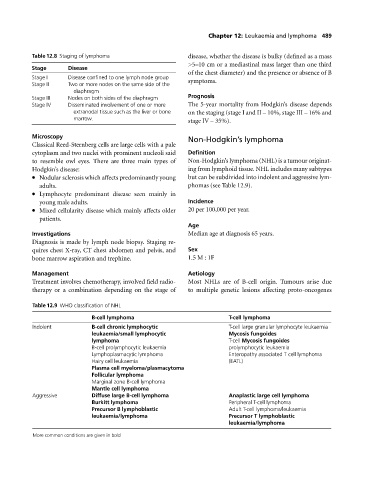
Table 12.8 Staging of lymphoma disease, whether the disease is bulky (defined as a mass
>5–10 cm or a mediastinal mass larger than one third
Stage Disease
of the chest diameter) and the presence or absence of B
Stage I Disease confined to one lymph node group symptoms.
Stage II Two or more nodes on the same side of the
diaphragm
Stage III Nodes on both sides of the diaphragm Prognosis
Stage IV Disseminated involvement of one or more The 5-year mortality from Hodgkin’s disease depends
extranodal tissue such as the liver or bone on the staging (stage I and II – 10%, stage III – 16% and
marrow. stage IV – 35%).
Microscopy Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Classical Reed-Sternberg cells are large cells with a pale
cytoplasm and two nuclei with prominent nucleoli said Definition
to resemble owl eyes. There are three main types of Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) is a tumour originat-
Hodgkin’s disease: ing from lymphoid tissue. NHL includes many subtypes
Nodular sclerosis which affects predominantly young
but can be subdivided into indolent and aggressive lym-
adults. phomas (see Table 12.9).
Lymphocyte predominant disease seen mainly in
young male adults. Incidence
Mixedcellularity disease which mainly affects older
20 per 100,000 per year.
patients.
Age
Investigations Median age at diagnosis 65 years.
Diagnosis is made by lymph node biopsy. Staging re-
quires chest X-ray, CT chest abdomen and pelvis, and Sex
bone marrow aspiration and trephine. 1.5 M : 1F
Management Aetiology
Treatment involves chemotherapy, involved field radio- Most NHLs are of B-cell origin. Tumours arise due
therapy or a combination depending on the stage of to multiple genetic lesions affecting proto-oncogenes
Table 12.9 WHO classification of NHL
B-cell lymphoma T-cell lymphoma
Indolent B-cell chronic lymphocytic T-cell large granular lymphocyte leukaemia
leukaemia/small lymphocytic Mycosis fungoides
lymphoma T-cell Mycosis fungoides
B-cell prolymphocytic leukaemia prolymphocytic leukaemia
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma
Hairy cell leukaemia (EATL)
Plasma cell myeloma/plasmacytoma
Follicular lymphoma
Marginal zone B-cell lymphoma
Mantle cell lymphoma
Aggressive Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Anaplastic large cell lymphoma
Burkitt lymphoma Peripheral T-cell lymphoma
Precursor B lymphoblastic Adult T-cell lymphoma/leukaemia
leukaemia/lymphoma Precursor T lymphoblastic
leukaemia/lymphoma
More common conditions are given in bold