Page 107 - Science
P. 107
RESEARCH | REPORT
and orthoIL-2Rb T cells. Stimulation of orthoIL- tained specificity for T regs modified to express the could, in principle, be achieved in any cell type
2Rb T cells (fig. S5B) with orthoIL-2 1G12 resulted orthoIL-2Rb,withpotency similartothatonCD8 + that also expresses the IL-2Rg.Activated mouse
in dose-dependent phosphorylation of STAT5 T cells (Fig. 2G and fig. S9, A and B). In addition B cells expressed the IL-2Rg but lacked appre-
(pSTAT5), a hallmark of IL-2R signaling, with to cells that naturally respond to IL-2, activation ciable levels of IL-2Rb (14, 15) and were relatively
potency similar to that of wild-type IL-2, but also of orthoIL-2Rb signaling pathways with orthoIL-2 insensitive to IL-2–dependent STAT5 activation
induced pSTAT5 on wild-type T cells, albeit with
significantly reduced potencyrelativetoIL-2
(Fig.1,GandI, and fig. S6). Bycomparison, WT-WT Ortho-WT Ortho-Ortho WT-Ortho 600000
orthoIL-2 3A10 was specific for orthoIL-2Rb 400000
T cells, but with a weaker potency relative to IL-2 200000 orthoIL-2R
(Fig. 1, G and I, and fig. S6). We speculated that IL-2 binding (MFI) 15000
orthoIL-2 1G12 activity on wild-type T cells is a 10000
consequence of weak residual binding to wild- 5000
0
type IL-2Rb (fig. S7). Low-affinity interactions WT
H134D Y135F
with IL-2Rb alone are enhanced in the presence Control T74Y T74V H134D Y135F R189E
of CD25 (8). Indeed, orthoIL-2 1G12 exhibited
binding to wild-type IL-2Rb when first captured WT-WT Ortho-WT Ortho-Ortho
Mutant Evolved
by CD25, with limited binding in the absence of
Site-directed Yeast evolution WT IL-2 IL-2 Library IL-2 Library
CD25 (figs. S1 and S8). OrthoIL-2 3A10 did not
bind appreciably to IL-2Rb even in the presence IL-2R
mutagenesis Discard
of CD25, in agreement with its negligible bio- WT binders
IL-2R orthoIL-2R orthoIL-2R
logical activity on CD25-positive T cells. Interac-
tion of orthoIL-2 1G12 and 3A10 with orthoIL-2Rb Strep-647 wt IL-2R orthoIL-2R CD25
wassignificantlyenhancedin thepresenceof CD25,
with apparent binding affinities of the ternary IL-2R :IL-2 orthoIL-2R :1G12 orthoIL-2R :3A10 Downloaded from
IL-2R
CD25/orthoIL-2Rb/orthoIL-2 complex that cor- (CD25)
relate with their respective potency on orthoIL- Q30
2Rb T cells (fig. S1). D34 L34 N30 L34 N30
In clinical ACT regimens, patient-derived T cells IL-2
E37 H37
for ACT are expanded in IL-2 before re-infusion in Y135 F135 A37 F135
order to obtain sufficient numbers of therapeutic H134 D134
M33 D134 V33 V33
cells with the desired genotype/phenotype (2). We E29 T36 E29 D29
Q36 K36
explored the in vitro activity of orthoIL-2 on ac-
+
tivated primary mouse CD8 T cells engineered IL-2R IL-2R http://science.sciencemag.org/
to express the orthoIL-2Rb and a yellow fluores-
+
cent protein (YFP) to distinguish modified (YFP ) IL-2 1G12 3A10 IL-2R orthoIL-2R
–
andunmodified(YFP ) cells (Fig. 2A). The tran-
scription factor STAT5 is phosphorylated upon ortho
T cell
IL-2 engagement with the IL-2R and translocates
to the nucleus, where it promotes the prolifera-
WT
tion and cell cycle progression of T cells (11). Wild- T cell SSC-A
type IL-2 induced the phosphorylation of STAT5 on March 1, 2018
(pSTAT5) in both wild-type and orthoIL-2Rb CD8 + pSTAT5
T cells with similar potency and signaling am-
WT ORTHO RATIO
plitude, indicating functional signal transduc-
AA # 29 30 33 34 36 37 41 EC 50 EC 50 (WT/ortho
tion through the wild-type receptor but not (pM) (pM) EC 50 )
orthoIL-2Rb (Fig. 2B). By comparison, orthoIL-2 WT E Q M D Q E R 3 3 1
1G12 potently activated STAT5 on orthoIL-2Rb– 1G12 N V L T H K 300 10 30
3A10 D N V L K A 1000 ortho
transduced T cells, with a potency increase by a
factor of ~5 relative to wild-type T cells. OrthoIL-2
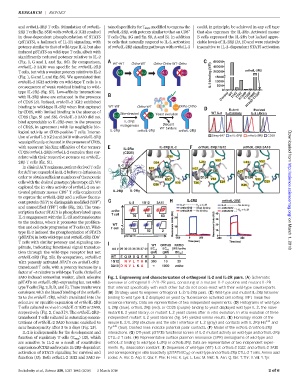
3A10 induced somewhat weaker, albeit selective Fig. 1. Engineering and characterization of orthogonal IL-2 and IL-2R pairs. (A) Schematic
pSTAT5 on orthoIL-2Rb–expressing but not wild- overview of orthogonal IL-2/IL-2R pairs, consisting of a mutant IL-2 cytokine and mutant IL-2R
type T cells (Fig.2,B,D,and E). These resultswere that interact specifically with each other but do not cross-react with their wild-type counterparts.
consistent with the biased binding of the orthoIL- (B) Strategy used to engineer orthogonal IL-2/IL-2Rb pairs. (C) Wild-type and mutant IL-2Rb tetramer
2s to the orthoIL-2Rb, which translated into the binding to wild-type IL-2 displayed on yeast by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. MFI, mean fluo-
selective or specific expansion of orthoIL-2Rb rescence intensity. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (D) Histograms of wild-type
T cells cultured ex vivo in orthoIL-2 1G12 or 3A10, IL-2Rb (blue), orthoIL-2Rb (red), or CD25 (purple) binding to yeast-displayed wild-type IL-2, the naïve
respectively (Fig. 2, C and D). The orthoIL-2Rb– mutant IL-2 yeast library, or mutant IL-2 yeast clones after in vitro evolution. In vitro evolution of three
transduced T cells cultured in saturating concen- independent mutant IL-2 yeast libraries (fig. S4) yielded similar results. (E) Homology model of the
trations of orthoIL-2 3A10 became enriched to mouse IL-2/IL-2Rb structure and the site I interface of IL-2 (gray) and contacts with IL-2Rb His 134 and
near homogeneity after 3 to 5 days (Fig. 2F). Tyr 135 (teal). Dashed lines indicate potential polar contacts. (F) Model of the orthoIL-2/orthoIL-2Rb
IL-2 is indispensable for the development and interactions. (G) Off-yeast pSTAT5 functional screen of IL-2 mutant activity on wild-type and orthoIL-2Rb
function of regulatory T cells (T regs )(12), which CTLL-2 T cells. (H) Representative surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensograms of wild-type and
are sensitive to IL-2 as a result of constitutive orthoIL-2 binding to wild-type IL-2Rb or orthoIL-2Rb. Data are representative of two independent experi-
expressionof CD25 and require IL-2Rb–dependent ments. K D , dissociation constant. (I) Sequences of wild-type (WT) IL-2, orthoIL-2 1G12, and orthoIL-2 3A10
activation of STAT5 signaling for survival and and corresponding in vitro bioactivity (pSTAT5 EC 50 ) on wild-type and orthoIL-2Rb CTLL-2 Tcells. Amino acid
function (13). Both orthoIL-2 1G12 and 3A10 re- codes: A, Ala; D, Asp; E, Glu; F, Phe; H, His; K, Lys; L, Leu; M, Met; N, Asn; Q, Gln; T, Thr; V, Val; Y, Tyr.
Sockolosky et al., Science 359, 1037–1042 (2018) 2 March 2018 2of6