Page 110 - Science
P. 110
RESEARCH | REPORT
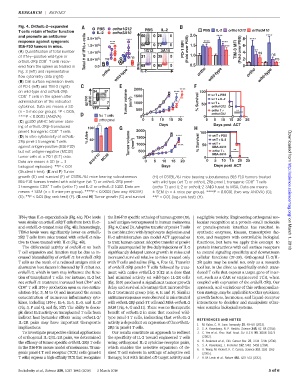
Fig. 4. OrthoIL-2–expanded PBS ortho1G12
T cells retain effector function IL-2 ortho3A10 PBS IL-2 PBS IL-2 ortho1G12 ortho3A10
and promote an antitumor 2.0 10 6 2.0 **** 8 ****
response against syngeneic + cells **** **** **** **** ****
B16-F10 tumors in mice. 1.5 10 6 PD-1 MFI 1.5 *** TIM-3 MFI 6
(A) Quantification of total number 1.0 10 6 * 1G12 3A10 (Fold over PBS) (Fold over PBS) 4 ** ns
of IFN-g–positive wild-type or Total # of IFN 5 ns ns 1.0 2 ns ns
+
orthoIL-2Rb CD8 T cells recov- 5.0 10
ered from the spleen as treated in 0.0 IFN 0.5 0
Fig. 3 (left) and representative ortho IL-2 ortho ortho
flow cytometry data (right). wild-type wild-type wild-type
(B) Cell surface expression levels
of PD-1 (left) and TIM-3 (right) 2000
on wild-type and orthoIL-2Rb **** **** 100
+
CD8 T cells in the spleen after 1500 wt T + PBS
administration of the indicated gp100 pMHC Tumor volume (mm 3 ) 1000 % Survival wt T + IL-2
wt T +
cytokines. Data are means ± SD 50 ortho1G12
YFP
(n = 5 mice per group). *P <0.05, 500 ortho T + **
ortho1G12
****P < 0.0001 (ANOVA). No T cells 0 0
ortho pmel 0 5 10 15 20 0 5 10 15 20 25
(C) gp100 pMHC tetramer stain-
** Days Days post ACT
ing of orthoIL-2Rb–transduced 100
+
pmel-1 transgenic CD8 Tcells. 2000 100
(D) In vitro cytotoxicity of orthoIL- % Alive 1500 **** wt T + PBS
2Rb pmel-1 transgenic T cells 50 Tumor volume (mm 3 ) 1000 % Survival wt T + IL-2
wt T +
against antigen-positive (B16-F10) **** 50 MSA-3A10 Downloaded from
but not antigen-negative (MC38) 0 500 ortho T + **
tumor cells at a 20:1 (E:T) ratio. B16-F10 MC38 0 0 MSA-3A10
Data are means ± SD (n =3 0 5 10 15 20 0 5 10 15 20 25
biological replicates). **P <0.01 Days Days post ACT
(Student t test). (E and F) Tumor
growth (E) and survival (F) of C57BL/6J mice bearing subcutaneous (H) of C57BL/6J mice bearing subcutaneous B16-F10 tumors treated
+
B16-F10 tumors treated with wild-type (wt T) or orthoIL-2Rb pmel- with wild-type (wt T) or orthoIL-2Rb pmel-1 transgenic CD8 Tcells
+
1 transgenic CD8 Tcells (ortho T) and IL-2 or orthoIL-2 1G12. Data are (ortho T) and IL-2 or orthoIL-2 3A10 fused to MSA. Data are means
means ± SEM (n = 5 mice per group). ****P < 0.0001 (two-way ANOVA) ±SEM (n = 4 mice per group). ****P < 0.0001 (two-way ANOVA) (G); http://science.sciencemag.org/
(E); **P < 0.01 (log-rank test) (F). (G and H) Tumor growth (G) and survival **P < 0.01 (log-rank test) (H).
IFN-g than IL-2–expanded cells (Fig. 4A). PD-1 levels the B16-F10 specific ortholog of human gp100 (19), negligible toxicity. Engineering orthogonal mo-
were similar on orthoIL-2Rb T cells from both IL-2– a self antigen overexpressed in human melanoma lecular recognition at a protein–small molecule
and orthoIL-2–treated mice (Fig. 4B). Interestingly, (Fig. 4, C and D). Adoptive transfer of pmel-1 T cells or protein-protein interface has resulted in
TIM-3 levels were significantly lower on orthoIL- in combination with lymphocyte depletion and synthetic enzymes, kinases, transcription fac- on March 1, 2018
2Rb T cells from mice treated with orthoIL-2 rela- IL-2 administration can model ACT approaches tors, and receptors with controllable biological
tive to those treated with IL-2 (Fig. 4B). to treat human cancer. Adoptive transfer of pmel-1 functions, but here we apply this concept to
The differential activity of orthoIL-2 on both T cells accompanied by five daily injections of IL-2 protein interactions with cell surface receptors
T cell expansion and function may be due to in- significantly delayed tumor growth in mice and to control signaling specificity and downstream
creased bioavailability of orthoIL-2 for orthoIL-2Rb increased survival relative to mice treated only cellular functions (21–28). Orthogonal IL-2/IL-
T cells as the result of a reduced antigen sink or with T cells and saline (Fig. 4, E to G). Transfer 2R pairs may be useful not only as a research
alternative host factors influenced by IL-2 but not of orthoIL-2Rb pmel-1 T cells followed by treat- tool but in the clinic to specifically enrich trans-
orthoIL-2, which in turn may influence the func- ment with native orthoIL-2 1G12 at a dose that duced T cells that express a target gene of inter-
tion of transplanted T cells. For instance, IL-2 but had minimal activity on wild-type IL-2R cells est, such as a CAR or engineered TCR, when
+
not orthoIL-2 treatment increased host CD4 and (fig. S10) produced a significant tumor growth coupled with expression of the orthoIL-2Rb.Our
+
CD8 TcellIFN-g production upon ex vivo restim- delay and survival advantage that mirrored the approach, and variations of this orthogonaliza-
ulation (Fig. 3, M to O) and increased the serum IL-2 treatment group (Fig. 4, E and F). Similar tion strategy, may be applicable to other cytokines,
concentration of numerous inflammatory cyto- antitumorresponseswere observedinmice treated growth factors, hormones, and ligand-receptor
kines, including IFN-g, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, and IL-13 with orthoIL-2Rb pmel-1 T cells and MSA–orthoIL-2 interactions to decipher and manipulate other-
(Fig.3, P andQ,and fig. S17).The abilitytodecou- 3A10 (Fig. 4, G and H). There was no therapeutic wise complex biological systems.
ple direct IL-2 activity on transplanted T cells from benefit of orthoIL-2 in mice that received wild-
indirect host bystander effects using orthoIL-2/ type pmel-1 T cells, indicating that orthoIL-2 REFERENCES AND NOTES
IL-2R pairs may have important therapeutic activity is dependent on expression of the orthoIL- 1. M. Kalos, C. H. June, Immunity 39,49–60 (2013).
implications. 2Rb in pmel-1 T cells. 2. S. A. Rosenberg, N. P. Restifo, Science 348,62–68 (2015).
To investigate prospective clinical applications Our results constitute an approach to redirect 3. C. Yee et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 16168–16173
of orthogonal IL-2/IL-2R pairs, we determined the specificity of IL-2 toward engineered T cells (2002).
4. R. Andersen et al., Clin. Cancer Res. 22, 3734–3745 (2016).
theefficacyoftumor-specific orthoIL-2Rb Tcells using orthogonal IL-2 cytokine-receptor pairs, 5. S. A. Rosenberg, J. Immunol. 192, 5451–5458 (2014).
in the B16-F10 mouse model of melanoma. Trans- which enables the selective expansion of de- 6. X. Wang, M. Rickert, K. C. Garcia, Science 310, 1159–1163
genic pmel-1 T cell receptor (TCR) cells (pmel-1 sired T cell subsets in settings of adoptive cell (2005).
T cells) express a high-affinity TCR that recognizes therapy, but with limited off-target activity and 7. A. M. Levin et al., Nature 484, 529–533 (2012).
Sockolosky et al., Science 359, 1037–1042 (2018) 2 March 2018 5of6