Page 183 - [Uma_Sekaran]_Research_methods_for_business__a_sk(BookZZ.org)
P. 183
MANAGERIAL IMPLICATIONS 167
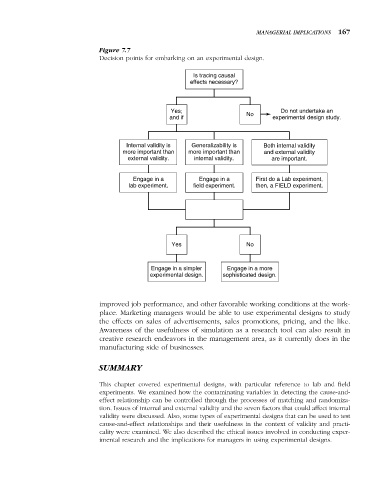
Figure 7.7
Decision points for embarking on an experimental design.
Is tracing causal
effects necessary?
Yes; No Do not undertake an
and if experimental design study.
Internal validity is Generalizability is Both internal validity
more important than more important than and external validity
external validity. internal validity. are important.
Engage in a Engage in a First do a Lab experiment,
lab experiment. field experiment. then, a FIELD experiment.
Are there cost
constraints?
Yes No
Engage in a simpler Engage in a more
experimental design. sophisticated design.
improved job performance, and other favorable working conditions at the work-
place. Marketing managers would be able to use experimental designs to study
the effects on sales of advertisements, sales promotions, pricing, and the like.
Awareness of the usefulness of simulation as a research tool can also result in
creative research endeavors in the management area, as it currently does in the
manufacturing side of businesses.
SUMMARY
This chapter covered experimental designs, with particular reference to lab and field
experiments. We examined how the contaminating variables in detecting the cause-and-
effect relationship can be controlled through the processes of matching and randomiza-
tion. Issues of internal and external validity and the seven factors that could affect internal
validity were discussed. Also, some types of experimental designs that can be used to test
cause-and-effect relationships and their usefulness in the context of validity and practi-
cality were examined. We also described the ethical issues involved in conducting exper-
imental research and the implications for managers in using experimental designs.