Page 55 - Cardiac Electrophysiology | A Modeling and Imaging Approach
P. 55
P. 55
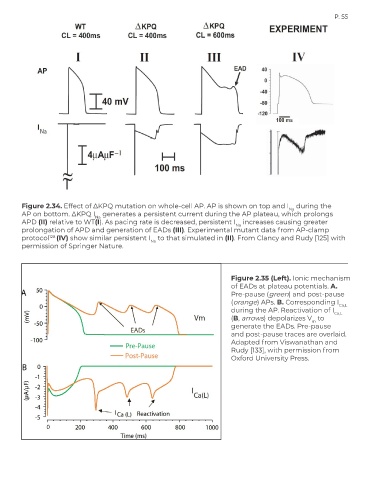
Figure 2.34. Effect of ∆KPQ mutation on whole-cell AP. AP is shown on top and I during the
Na
AP on bottom. ∆KPQ I generates a persistent current during the AP plateau, which prolongs
Na
APD (II) relative to WT(I). As pacing rate is decreased, persistent I increases causing greater
Na
prolongation of APD and generation of EADs (III). Experimental mutant data from AP-clamp
protocol 128 (IV) show similar persistent I to that simulated in (II). From Clancy and Rudy [125] with
Na
permission of Springer Nature.
Figure 2.35 (Left). Ionic mechanism
of EADs at plateau potentials. A.
Pre-pause (green) and post-pause
(orange) APs. B. Corresponding I Ca,L
during the AP. Reactivation of I Ca,L
(B, arrows) depolarizes V to
m
generate the EADs. Pre-pause
and post-pause traces are overlaid.
Adapted from Viswanathan and
Rudy [133], with permission from
Oxford University Press.