Page 129 - ACFE Fraud Reports 2009_2020
P. 129
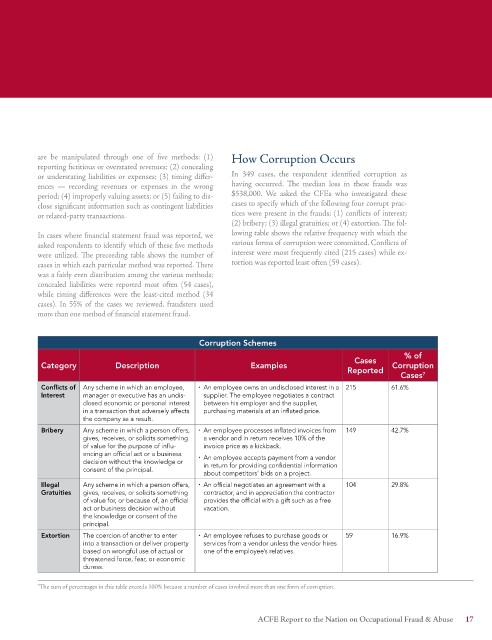
are be manipulated through one of five methods: (1) How Corruption Occurs
reporting fictitious or overstated revenues; (2) concealing
or understating liabilities or expenses; (3) timing differ- In 349 cases, the respondent identified corruption as
ences — recording revenues or expenses in the wrong having occurred. The median loss in these frauds was
period; (4) improperly valuing assets; or (5) failing to dis- $538,000. We asked the CFEs who investigated these
close significant information such as contingent liabilities cases to specify which of the following four corrupt prac-
or related-party transactions. tices were present in the frauds: (1) conflicts of interest;
(2) bribery; (3) illegal gratuities; or (4) extortion. The fol-
In cases where financial statement fraud was reported, we lowing table shows the relative frequency with which the
asked respondents to identify which of these five methods various forms of corruption were committed. Conflicts of
were utilized. The preceeding table shows the number of interest were most frequently cited (215 cases) while ex-
cases in which each particular method was reported. There tortion was reported least often (59 cases).
was a fairly even distribution among the various methods;
concealed liabilities were reported most often (54 cases),
while timing differences were the least-cited method (34
cases). In 55% of the cases we reviewed, fraudsters used
more than one method of financial statement fraud.
Corruption Schemes
% of
Cases
Category Description Examples Corruption
Reported
Cases 7
Conflicts of Any scheme in which an employee, ¨ An employee owns an undisclosed interest in a 215 61.6%
Interest manager or executive has an undis- supplier. The employee negotiates a contract
closed economic or personal interest between his employer and the supplier,
in a transaction that adversely affects purchasing materials at an inflated price.
the company as a result.
Bribery Any scheme in which a person offers, ¨ An employee processes inflated invoices from 149 42.7%
gives, receives, or solicits something a vendor and in return receives 10% of the
of value for the purpose of influ- invoice price as a kickback.
encing an official act or a business ¨ An employee accepts payment from a vendor
decision without the knowledge or in return for providing confidential information
consent of the principal.
about competitors’ bids on a project.
Illegal Any scheme in which a person offers, ¨ An official negotiates an agreement with a 104 29.8%
Gratuities gives, receives, or solicits something contractor, and in appreciation the contractor
of value for, or because of, an official provides the official with a gift such as a free
act or business decision without vacation.
the knowledge or consent of the
principal.
Extortion The coercion of another to enter ¨ An employee refuses to purchase goods or 59 16.9%
into a transaction or deliver property services from a vendor unless the vendor hires
based on wrongful use of actual or one of the employee’s relatives.
threatened force, fear, or economic
duress.
7 The sum of percentages in this table exceeds 100% because a number of cases involved more than one form of corruption.
ACFE Report to the Nation on Occupational Fraud & Abuse 1