Page 33 - Differential Diagnosis in Small Animal Cytology, The Skin and Subcutis
P. 33
Chapt
er 3
20
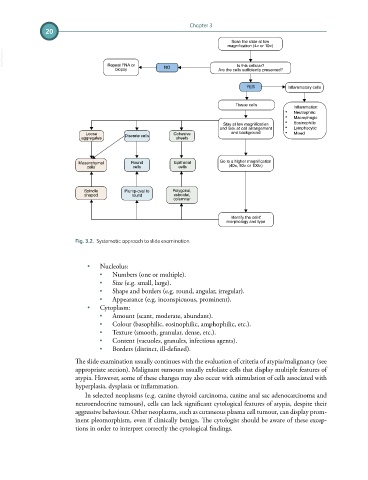
Scan the slide at low
magnification (4× or 10×)
VetBooks.ir
Repeat FNA or
Is this cellular?
biopsy NO Are the cells sufficiently preserved?
YES Inflammatory cells
Tissue cells
Inflammation:
• Neutrophilic
• Macrophagic
Stay at low magnification • Eosinophilic
and look at cell arrangement • Lymphocytic
Loose Cohesive and background • Mixed
aggregates Discrete cells sheets
Mesenchymal Round Epithelial Go to a higher magnification
(40×, 50× or 100×)
cells cells cells
Spindle Plump-oval to Polygonal,
shaped round cuboidal,
columnar
Identify the cells'
morphology and type
Fig. 3.2. Systematic approach to slide examination.
• Nucleolus:
• Numbers (one or multiple).
• Size (e.g. small, large).
• Shape and borders (e.g. round, angular, irregular).
• Appearance (e.g. inconspicuous, prominent).
• Cytoplasm:
• Amount (scant, moderate, abundant).
• Colour (basophilic, eosinophilic, amphophilic, etc.).
• Texture (smooth, granular, dense, etc.).
• Content (vacuoles, granules, infectious agents).
• Borders (distinct, ill-defined).
The slide examination usually continues with the evaluation of criteria of atypia/malignancy (see
appropriate section). Malignant tumours usually exfoliate cells that display multiple features of
atypia. However, some of these changes may also occur with stimulation of cells associated with
hyperplasia, dysplasia or inflammation.
In selected neoplasms (e.g. canine thyroid carcinoma, canine anal sac adenocarcinoma and
neuroendocrine tumours), cells can lack significant cytological features of atypia, despite their
aggressive behaviour. Other neoplasms, such as cutaneous plasma cell tumour, can display prom-
inent pleomorphism, even if clinically benign. The cytologist should be aware of these excep-
tions in order to interpret correctly the cytological findings.