Page 1169 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 1169
1144 CHAPTER 11
VetBooks.ir NEONATAL AND CONGENITAL OCULAR DISORDERS
Ocular diseases of the foal may be congenital or
sure to toxins during gestation. Thoroughbreds have
acquired. Congenital ocular defects have a reported including intrauterine maternal infections and expo-
incidence of 0.5–35% in the horse (depending on the been reported to be at higher risk, although an inher-
population studied). Foals may be born with single or ited component has yet to be confirmed.
multiple ocular defects including NLS atresia, entro- These anomalies occur when the neuroectoderm
pion, eyelid, iris or fundic colobomas, anterior seg- of the primary optic vesicle fails to develop properly
ment dysgenesis, cataracts, microphthalmia, retinal from the anterior neural plate of the neural tube dur-
dysplasia, retinal detachment and CSNB. Cataracts ing embryonic development. Disfigurement of the
are the most frequently reported congenital lesions in orbit may occur secondary to an absent or smaller
foals. Congenital defects must be differentiated from than normal-sized globe.
acquired lesions or disorders such as ocular trauma,
globe perforation and phthisis bulbi. Clinical presentation
Normal foals have decreased corneal sensitiv- Affected foals are born with an apparent absence of
ity and lower tear production than adult horses. ocular tissue or a small eye, which is usually obvi-
Additionally, their menace reflex may not appear ous on examination. A small palpebral fissure, an
until 7–14 days post partum. These factors make elevated/prominent nictitating membrane, con-
foals, especially those that are systemically ill and/ junctivitis and facial asymmetry may also be noted
or recumbent, prone to acquired ocular disease. (Fig. 11.39). Entropion may occur secondary to fail-
All compromised neonatal foals should be exam- ure of the smaller than normal globe to support the
ined daily for signs of ocular disease or ulceration. eyelids and may result in mild keratitis to severe cor-
Ophthalmic lubricant ointments should be admin- neal ulceration. Vision may be present, but usually
istered regularly to help protect the cornea from the eye is blind. Multiple ocular anomalies may also
damage. be present, including colobomas, cataracts, retinal
dysplasia and/or retinal detachment.
ANOPHTHALMOS AND
MICROPHTHALMOS
Definition/overview
Anophthalmos is a very rare condition that involves 11.39
the complete absence of ocular tissues, resulting in
blindness. Microphthalmos describes a congeni-
tally small globe and can be subdivided into simple
or pure microphthalmos (or nanophthalmos) and
complicated microphthalmos. Pure microphthal-
mos involves a small but otherwise normal and
visual globe. Complicated microphthalmos is more
common and involves a congenitally small globe in
combination with multiple anterior and/or posterior
segment defects that may have an effect on vision.
One or both eyes may be affected.
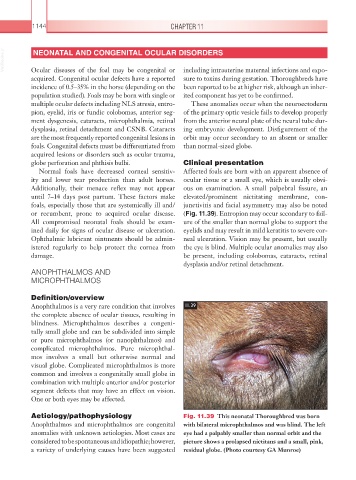
Aetiology/pathophysiology Fig. 11.39 This neonatal Thoroughbred was born
Anophthalmos and microphthalmos are congenital with bilateral microphthalmos and was blind. The left
anomalies with unknown aetiologies. Most cases are eye had a palpably smaller than normal orbit and the
considered to be spontaneous and idiopathic; however, picture shows a prolapsed nictitans and a small, pink,
a variety of underlying causes have been suggested residual globe. (Photo courtesy GA Munroe)