Page 1191 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 1191
1166 CHAPTER 11
VetBooks.ir 11.70 11.71
Figs. 11.70, 11.71 Squamous cell carcinoma of the nictitans. (11.70) Only the leading edge of the nictitans
appears affected. (11.71) With retropulsion of the globe, the nictitans is elevated, demonstrating deeper tissue
involvement.
fibromas, fibrosarcomas, lymphomas, lymphosarco-
11.72
mas, histiocytomas, schwannomas, angiosarcomas,
neurofibromas, trichoepitheliomas, haemangiomas,
haemangiosarcomas, myxosarcomas and plasma cell
tumours.
Diagnosis
SCC should be considered with any persistent pro-
liferative or ulcerative eyelid lesion. The clinical
appearance may be suggestive, but definitive diagno-
sis is based on cytology (fine-needle aspirate [FNA]
or scrapings) or histology (incisional/wedge or exci-
sional biopsy). This typically shows cords and/or
islands of polyhedral cells with intercellular bridges,
lack of basal lamina, keratinised ‘pearls’ and mitotic
figures. The use of urinalysis test strips to detect
occult blood in the tears in order to differentiate
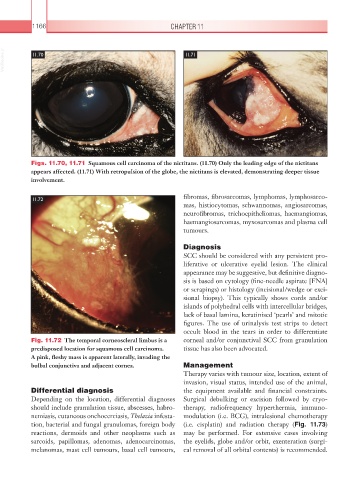
Fig. 11.72 The temporal corneoscleral limbus is a corneal and/or conjunctival SCC from granulation
predisposed location for squamous cell carcinoma. tissue has also been advocated.
A pink, fleshy mass is apparent laterally, invading the
bulbal conjunctiva and adjacent cornea. Management
Therapy varies with tumour size, location, extent of
invasion, visual status, intended use of the animal,
Differential diagnosis the equipment available and financial constraints.
Depending on the location, differential diagnoses Surgical debulking or excision followed by cryo-
should include granulation tissue, abscesses, habro- therapy, radiofrequency hyperthermia, immuno-
nemiasis, cutaneous onchocerciasis, Thelazia infesta- modulation (i.e. BCG), intralesional chemotherapy
tion, bacterial and fungal granulomas, foreign body (i.e. cisplatin) and radiation therapy (Fig. 11.73)
reactions, dermoids and other neoplasms such as may be performed. For extensive cases involving
sarcoids, papillomas, adenomas, adenocarcinomas, the eyelids, globe and/or orbit, exenteration (surgi-
melanomas, mast cell tumours, basal cell tumours, cal removal of all orbital contents) is recommended.