Page 1319 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 1319
1294 CHAPTER 12
VetBooks.ir 12.104 12.105
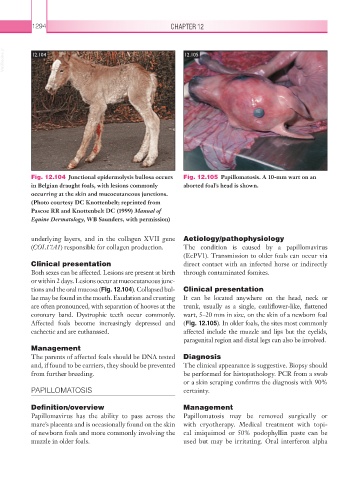
Fig. 12.104 Junctional epidermolysis bullosa occurs Fig. 12.105 Papillomatosis. A 10-mm wart on an
in Belgian draught foals, with lesions commonly aborted foal’s head is shown.
occurring at the skin and mucocutaneous junctions.
(Photo courtesy DC Knottenbelt; reprinted from
Pascoe RR and Knottenbelt DC (1999) Manual of
Equine Dermatology, WB Saunders, with permission)
underlying layers, and in the collagen XVII gene Aetiology/pathophysiology
(COL17A1) responsible for collagen production. The condition is caused by a papillomavirus
(EcPV1). Transmission to older foals can occur via
Clinical presentation direct contact with an infected horse or indirectly
Both sexes can be affected. Lesions are present at birth through contaminated fomites.
or within 2 days. Lesions occur at mucocutaneous junc-
tions and the oral mucosa (Fig. 12.104). Collapsed bul- Clinical presentation
lae may be found in the mouth. Exudation and crusting It can be located anywhere on the head, neck or
are often pronounced, with separation of hooves at the trunk, usually as a single, cauliflower-like, flattened
coronary band. Dystrophic teeth occur commonly. wart, 5–20 mm in size, on the skin of a newborn foal
Affected foals become increasingly depressed and (Fig. 12.105). In older foals, the sites most commonly
cachectic and are euthanased. affected include the muzzle and lips but the eyelids,
paragenital region and distal legs can also be involved.
Management
The parents of affected foals should be DNA tested Diagnosis
and, if found to be carriers, they should be prevented The clinical appearance is suggestive. Biopsy should
from further breeding. be performed for histopathology. PCR from a swab
or a skin scraping confirms the diagnosis with 90%
PAPILLOMATOSIS certainty.
Definition/overview Management
Papillomavirus has the ability to pass across the Papillomatosis may be removed surgically or
mare’s placenta and is occasionally found on the skin with cryotherapy. Medical treatment with topi-
of newborn foals and more commonly involving the cal imiquimod or 50% podophyllin paste can be
muzzle in older foals. used but may be irritating. Oral interferon alpha