Page 1106 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 1106
1072 Chapter 10
VetBooks.ir
A B
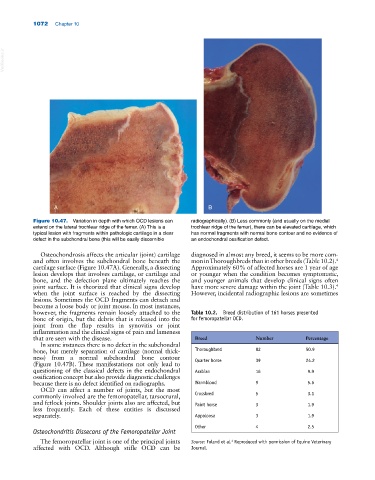
Figure 10.47. Variation in depth with which OCD lesions can radiographically). (B) Less commonly (and usually on the medial
extend on the lateral trochlear ridge of the femur. (A) This is a trochlear ridge of the femur), there can be elevated cartilage, which
typical lesion with fragments within pathologic cartilage in a clear has normal fragments with normal bone contour and no evidence of
defect in the subchondral bone (this will be easily discernible an endochondral ossification defect.
Osteochondrosis affects the articular (joint) cartilage diagnosed in almost any breed, it seems to be more com
and often involves the subchondral bone beneath the mon in Thoroughbreds than in other breeds (Table 10.2).
4
cartilage surface (Figure 10.47A). Generally, a dissecting Approximately 60% of affected horses are 1 year of age
lesion develops that involves cartilage, or cartilage and or younger when the condition becomes symptomatic,
bone, and the defection plane ultimately reaches the and younger animals that develop clinical signs often
joint surface. It is theorized that clinical signs develop have more severe damage within the joint (Table 10.3).
4
when the joint surface is reached by the dissecting However, incidental radiographic lesions are sometimes
lesions. Sometimes the OCD fragments can detach and
become a loose body or joint mouse. In most instances,
however, the fragments remain loosely attached to the Table 10.2. Breed distribution of 161 horses presented
bone of origin, but the debris that is released into the for femoropatellar OCD.
joint from the flap results in synovitis or joint
inflammation and the clinical signs of pain and lameness
that are seen with the disease. Breed Number Percentage
In some instances there is no defect in the subchondral
bone, but merely separation of cartilage (normal thick Thoroughbred 82 50.9
ness) from a normal subchondral bone contour
(Figure 10.47B). These manifestations not only lead to Quarter horse 39 24.2
questioning of the classical defects in the endochondral Arabian 16 9.9
ossification concept but also provide diagnostic challenges
because there is no defect identified on radiographs. Warmblood 9 5.6
OCD can affect a number of joints, but the most
commonly involved are the femoropatellar, tarsocrural, Crossbred 5 3.1
and fetlock joints. Shoulder joints also are affected, but Paint horse 3 1.9
less frequently. Each of these entities is discussed
separately. Appaloosa 3 1.9
Other 4 2.5
Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Femoropatellar Joint
The femoropatellar joint is one of the principal joints Source: Foland et al. Reproduced with permission of Equine Veterinary
4
affected with OCD. Although stifle OCD can be Journal.