Page 398 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 398
364 Chapter 3
VetBooks.ir
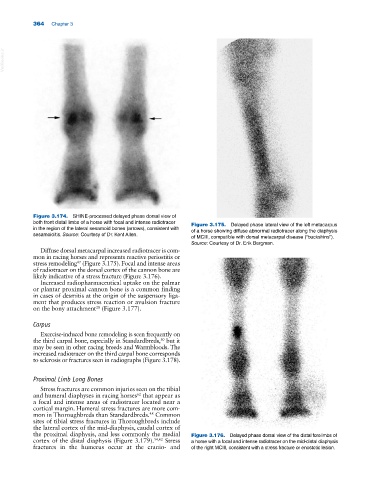
Figure 3.174. SHINE‐processed delayed phase dorsal view of
both front distal limbs of a horse with focal and intense radiotracer Figure 3.175. Delayed phase lateral view of the left metacarpus
in the region of the lateral sesamoid bones (arrows), consistent with of a horse showing diffuse abnormal radiotracer along the diaphysis
sesamoiditis. Source: Courtesy of Dr. Kent Allen. of MCIII, compatible with dorsal metacarpal disease (“buckshins”).
Source: Courtesy of Dr. Erik Bergman.
Diffuse dorsal metacarpal increased radiotracer is com
mon in racing horses and represents reactive periostitis or
stress remodeling (Figure 3.175). Focal and intense areas
47
of radiotracer on the dorsal cortex of the cannon bone are
likely indicative of a stress fracture (Figure 3.176).
Increased radiopharmaceutical uptake on the palmar
or plantar proximal cannon bone is a common finding
in cases of desmitis at the origin of the suspensory liga
ment that produces stress reaction or avulsion fracture
28
on the bony attachment (Figure 3.177).
Carpus
Exercise‐induced bone remodeling is seen frequently on
the third carpal bone, especially in Standardbreds, but it
30
may be seen in other racing breeds and Warmbloods. The
increased radiotracer on the third carpal bone corresponds
to sclerosis or fractures seen in radiographs (Figure 3.178).
Proximal Limb Long Bones
Stress fractures are common injuries seen on the tibial
and humeral diaphyses in racing horses that appear as
62
a focal and intense areas of radiotracer located near a
cortical margin. Humeral stress fractures are more com
mon in Thoroughbreds than Standardbreds. Common
48
sites of tibial stress fractures in Thoroughbreds include
the lateral cortex of the mid‐diaphysis, caudal cortex of
the proximal diaphysis, and less commonly the medial Figure 3.176. Delayed phase dorsal view of the distal forelimbs of
cortex of the distal diaphysis (Figure 3.179). 54,62 Stress a horse with a focal and intense radiotracer on the mid‐distal diaphysis
fractures in the humerus occur at the cranio‐ and of the right MCIII, consistent with a stress fracture or enostotic lesion.