Page 186 - Basic Monitoring in Canine and Feline Emergency Patients
P. 186
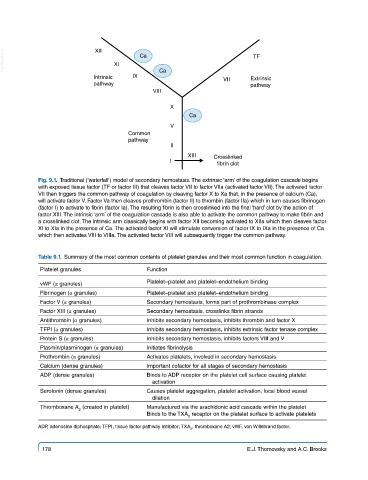
VetBooks.ir XII XI Ca TF
Intrinsic IX Ca VII Extrinsic
pathway pathway
VIII
X
Ca
V
Common
pathway
II
XIII Crosslinked
I
fibrin clot
Fig. 9.1. Traditional (‘waterfall’) model of secondary hemostasis. The extrinsic ‘arm’ of the coagulation cascade begins
with exposed tissue factor (TF or factor III) that cleaves factor VII to factor VIIa (activated factor VII). The activated factor
VII then triggers the common pathway of coagulation by cleaving factor X to Xa that, in the presence of calcium (Ca),
will activate factor V. Factor Va then cleaves prothrombin (factor II) to thrombin (factor IIa) which in turn causes fibrinogen
(factor I) to activate to fibrin (factor Ia). The resulting fibrin is then crosslinked into the final ‘hard’ clot by the action of
factor XIII. The intrinsic ‘arm’ of the coagulation cascade is also able to activate the common pathway to make fibrin and
a crosslinked clot. The intrinsic arm classically begins with factor XII becoming activated to XIIa which then cleaves factor
XI to XIa in the presence of Ca. The activated factor XI will stimulate conversion of factor IX to IXa in the presence of Ca
which then activates VIII to VIIIa. The activated factor VIII will subsequently trigger the common pathway.
Table 9.1. Summary of the most common contents of platelet granules and their most common function in coagulation.
Platelet granules Function
vWF (α granules) Platelet–platelet and platelet–endothelium binding
Fibrinogen (α granules) Platelet–platelet and platelet–endothelium binding
Factor V (α granules) Secondary hemostasis, forms part of prothrombinase complex
Factor XIII (α granules) Secondary hemostasis, crosslinks fibrin strands
Antithrombin (α granules) Inhibits secondary hemostasis, inhibits thrombin and factor X
TFPI (α granules) Inhibits secondary hemostasis, inhibits extrinsic factor tenase complex
Protein S (α granules) Inhibits secondary hemostasis, inhibits factors VIII and V
Plasmin/plasminogen (α granules) Initiates fibrinolysis
Prothrombin (α granules) Activates platelets, involved in secondary hemostasis
Calcium (dense granules) Important cofactor for all stages of secondary hemostasis
ADP (dense granules) Binds to ADP receptor on the platelet cell surface causing platelet
activation
Serotonin (dense granules) Causes platelet aggregation, platelet activation, local blood vessel
dilation
Thromboxane A (created in platelet) Manufactured via the arachidonic acid cascade within the platelet
2
Binds to the TXA receptor on the platelet surface to activate platelets
2
ADP, adenosine diphosphate; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor; TXA , thromboxane A2; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
2
178 E.J. Thomovsky and A.C. Brooks