Page 190 - Basic Monitoring in Canine and Feline Emergency Patients
P. 190
means a large amount of fibrinogen can be cleaved to of fibrin only occurs in clots. Fibrin degradation
fibrin. The fibrin is stimulated by factor XIII to cross- products that are made from breakdown of
VetBooks.ir link the platelets and create the firm ‘final’ clot. crosslinked fibrin are called d-dimers and indicate
breakdown of an actual clot (not just fibrin/fibrino-
Fibrinolysis gen) is occurring. Therefore, measurement of ele-
vated d-dimers can sometimes be used to indicate
One of the most interesting things about coagula- the presence of a thrombotic event.
tion is that while it is ramping up to form a clot, However, since clot stability is also needed to
negative feedback processes are almost immediately control bleeding, there are also fibrinolysis inhibi-
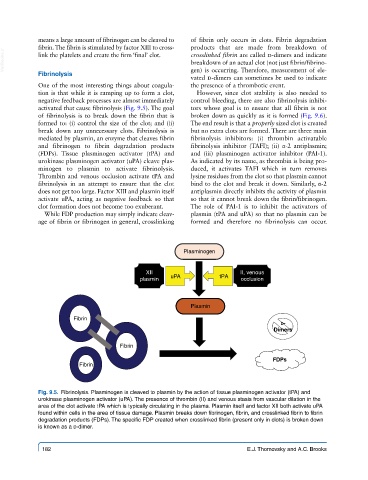
activated that cause fibrinolysis (Fig. 9.5). The goal tors whose goal is to ensure that all fibrin is not
of fibrinolysis is to break down the fibrin that is broken down as quickly as it is formed (Fig. 9.6).
formed to: (i) control the size of the clot; and (ii) The end result is that a properly sized clot is created
break down any unnecessary clots. Fibrinolysis is but no extra clots are formed. There are three main
mediated by plasmin, an enzyme that cleaves fibrin fibrinolysis inhibitors: (i) thrombin activatable
and fibrinogen to fibrin degradation products fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI); (ii) α-2 antiplasmin;
(FDPs). Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and and (iii) plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1).
urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) cleave plas- As indicated by its name, as thrombin is being pro-
minogen to plasmin to activate fibrinolysis. duced, it activates TAFI which in turn removes
Thrombin and venous occlusion activate tPA and lysine residues from the clot so that plasmin cannot
fibrinolysis in an attempt to ensure that the clot bind to the clot and break it down. Similarly, α-2
does not get too large. Factor XIII and plasmin itself antiplasmin directly inhibits the activity of plasmin
activate uPA, acting as negative feedback so that so that it cannot break down the fibrin/fibrinogen.
clot formation does not become too exuberant. The role of PAI-1 is to inhibit the activators of
While FDP production may simply indicate cleav- plasmin (tPA and uPA) so that no plasmin can be
age of fibrin or fibrinogen in general, crosslinking formed and therefore no fibrinolysis can occur.
Plasminogen
XII II, venous
plasmin uPA tPA occlusion
Plasmin
Fibrin
D-
Dimers
Fibrin
FDPs
Fibrin
Fig. 9.5. Fibrinolysis. Plasminogen is cleaved to plasmin by the action of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and
urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA). The presence of thrombin (II) and venous stasis from vascular dilation in the
area of the clot activate tPA which is typically circulating in the plasma. Plasmin itself and factor XII both activate uPA
found within cells in the area of tissue damage. Plasmin breaks down fibrinogen, fibrin, and crosslinked fibrin to fibrin
degradation products (FDPs). The specific FDP created when crosslinked fibrin (present only in clots) is broken down
is known as a d-dimer.
182 E.J. Thomovsky and A.C. Brooks